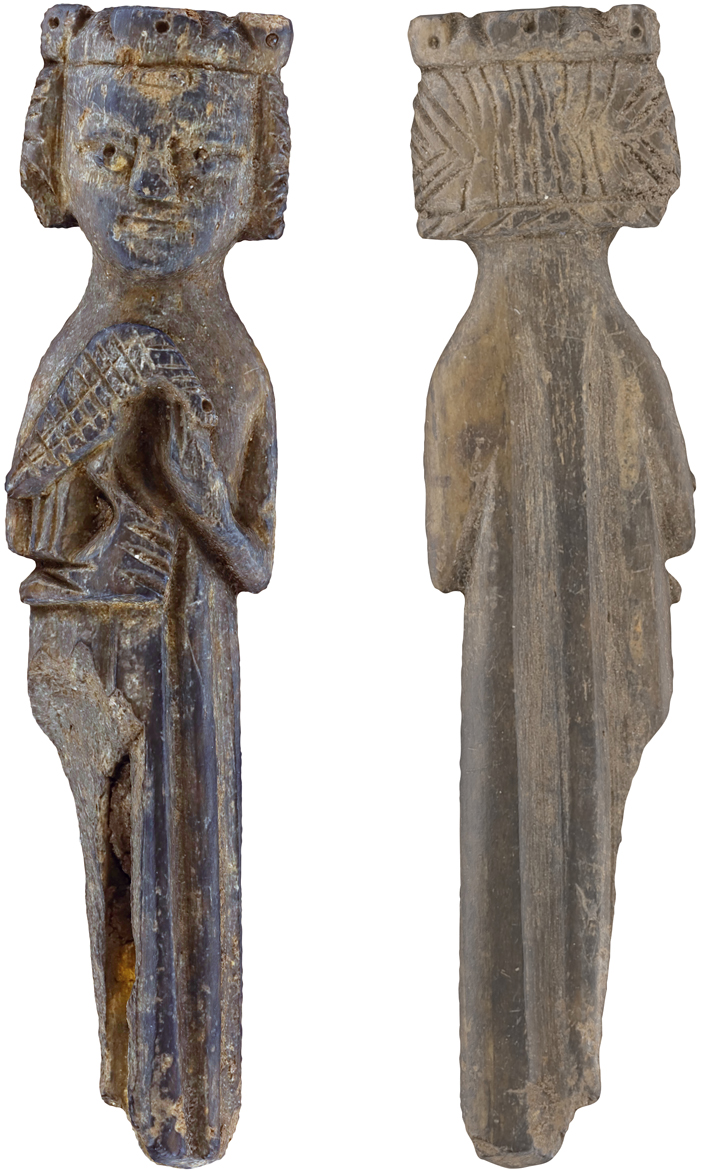
OSLO, NORWAY—According to a statement released by the University of Oslo, researcher Johan Bollaert has studied Norway’s medieval inscriptions, some of which were written with letters of the Roman alphabet, and some of which were written with runes. He noted that carving words into wood, stone, or metal takes time and effort, and so inscriptions are therefore shorter and simpler forms of text, and are usually found in places where the context would have been understood, such as on gravestones. The analysis showed that inscriptions written with letters and with runes both featured punctuation, a carefully planned layout, and ornamentation, although letters, which were introduced to Norway with Christianity, were more often used in inscriptions in cities and episcopal seats where bishops resided. These texts were also more standardized and may have been produced in workshops affiliated with the church. In contrast, a lot of variation was found among runic inscriptions, which were more likely to be placed in smaller settlements. Gravestones inscribed with letters often had an image of the deceased, while gravestones with runic inscriptions did not, suggesting that a high rate of runic literacy was expected, Bollaert concluded. To read about a stone unearthed in Sweden with the longest existing runic inscription, go to "The Emperor of Stones."