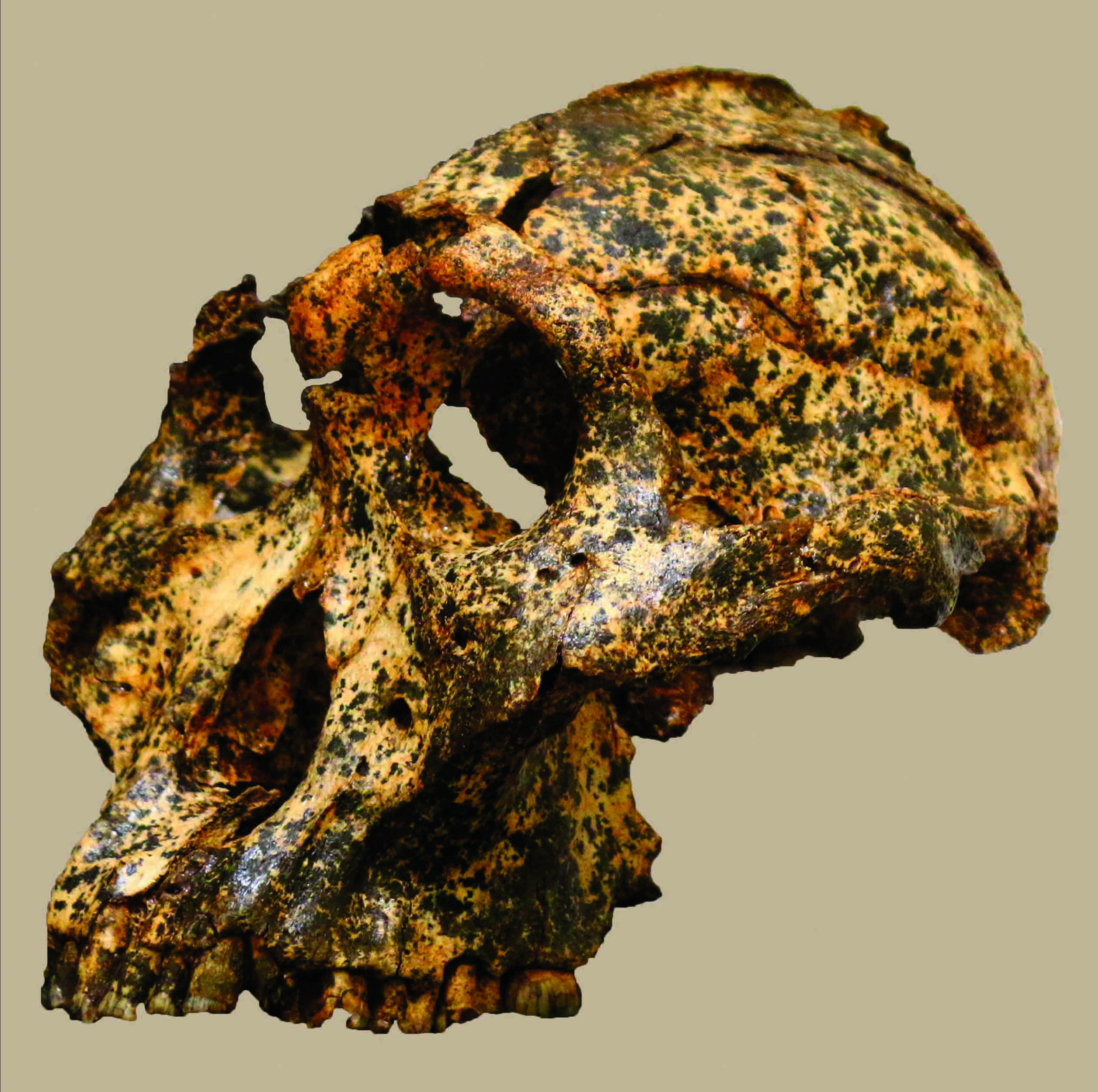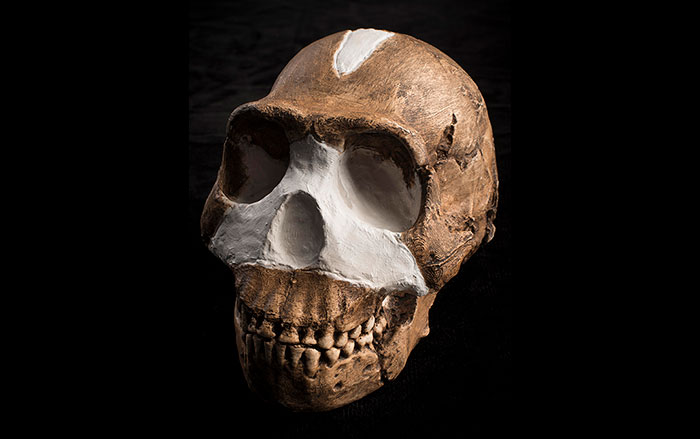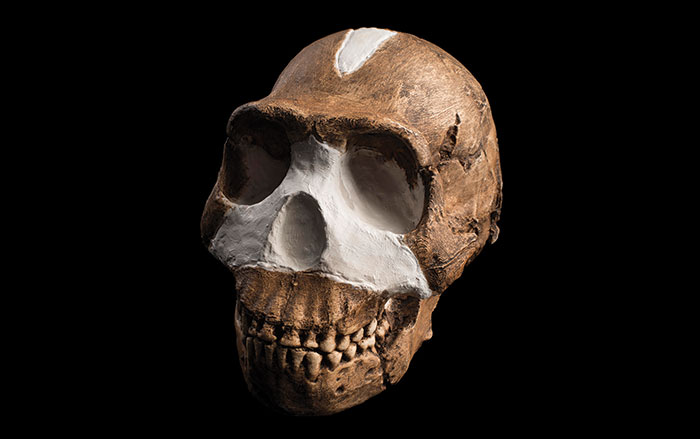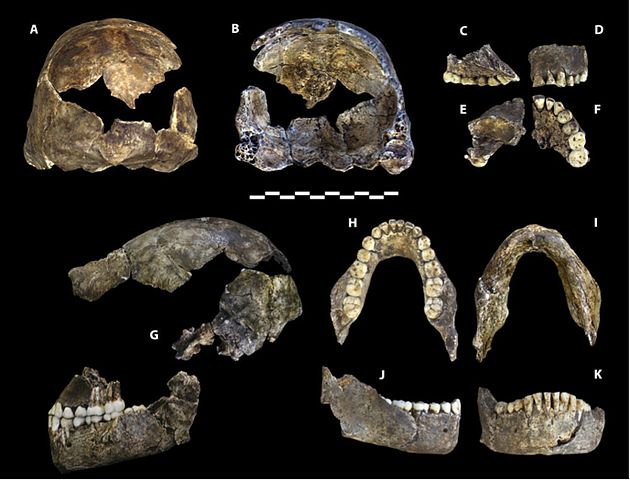
JOHANNESBURG, SOUTH AFRICA—According to a report in BBC News, Lee Berger of Wits University says the fossilized remains of Homo naledi, discovered in a remote chamber in South Africa’s Rising Star cave system, may be between 200,000 and 300,000 years old. When the specimens were discovered in 2015, Berger thought they could be up to three million years old. The new dates suggest that Homo naledi, which exhibits some traits similar to the genus Australopithecus, and some traits found in the genus Homo, could have overlapped with modern humans. “These look like a primitive form of our own genus—Homo,” said Berger’s colleague, John Hawks of the University of Wisconsin. “It looks like it might be connected to early Homo erectus, or Homo habilis, Homo rudolfensis,” he said. Berger thinks the Homo naledi remains could have been placed in the hard-to-reach chamber deliberately, which would suggest that the small-brained hominins were capable of ritual behavior. To read more about Homo naledi, go to “A New Human Relative.”