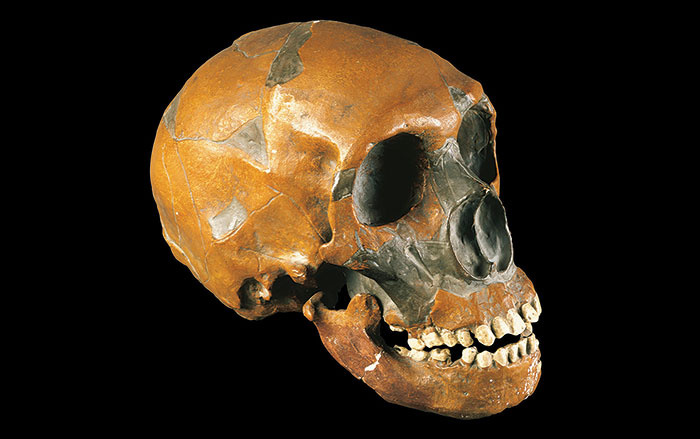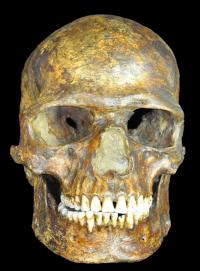
COPENHAGEN, DENMARK—DNA from the ulna of a modern human skeleton discovered in 1954 at an archaeological site at Kostenki-Borshchevo, located in southwest Russia, has been mapped by a team of scientists led by evolutionary biologist Eske Wilerslev of the Natural History Museum at the University of Copenhagen. The skeleton has been dated to between 36,200 and 38,700 years old, making the genome the second oldest to be sequenced. This new data suggests that this man, who had dark skin and dark eyes, had DNA from Europe’s indigenous hunter-gatherers, people from the Middle East who later became early farmers, and western Asians. It had been thought that these three groups only mixed in the past 5,000 years. “What is surprising is this guy represents one of the earliest Europeans, but at the same time he basically contains all the genetic components that you find in contemporary Europeans—at 37,000 years ago,” Willerslev told Science. The man, known as Kostenki XIV and as Markina Gora, also had about one percent more Neanderthal DNA than today’s Europeans and Asians, from modern human and Neanderthal contact more than 45,000 years ago. “In principle, you just have sex with your neighbor and they have it with their next neighbor—you don’t need to have these armies of people moving around to spread the genes,” Willerslev explained. To read more about paleogenetics, see "Neanderthal Genome Decoded."