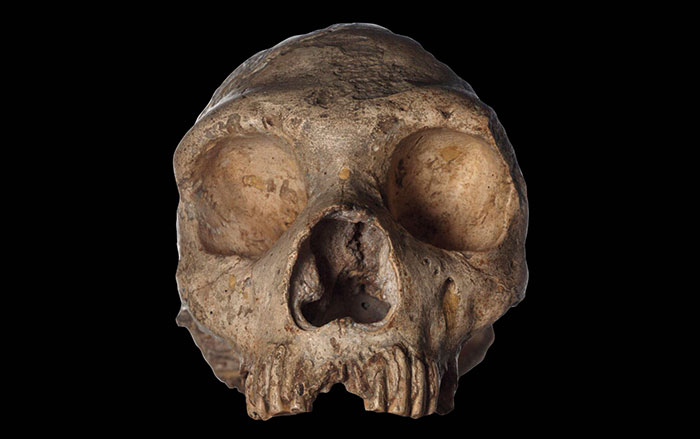
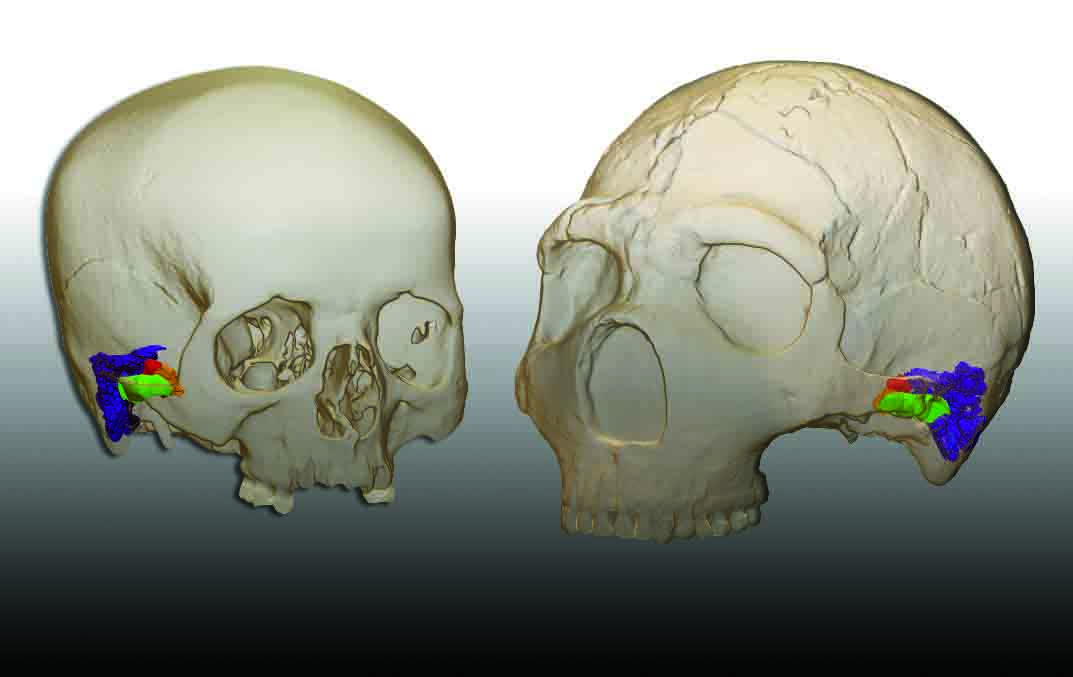
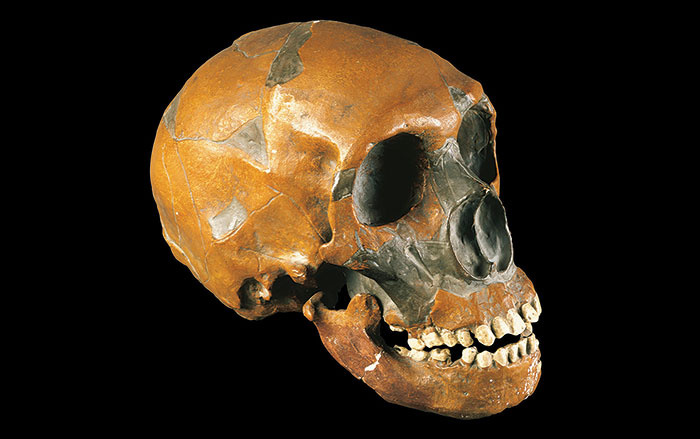
OXFORD, ENGLAND—According to a statement released by the University of Oxford, Greger Larson and his colleagues developed a metric using genetic distances to predict fertility in the offspring of crosses between any two mammal species. The study suggests that the genetic difference between ancient modern humans, Neanderthals, and Denisovans was so small that their hybrid offspring would have likely been healthy and fertile, explaining the presence of traces of Neanderthal and Denisovan DNA in the modern human genome today. The researchers found that the greater the evolutionary distance between two mammal species, the less likely the match is to produce fertile offspring. Overall, the genetic distance values between early modern humans, Neanderthals, and Denisovans were smaller than those recorded between polar bears and brown bears, which are known to produce healthy, fertile young. To read more about interbreeding between Neanderthals and Denisovans, go to "Hominin Hybrid," one of ARCHAEOLOGY's Top 10 Discoveries of 2018.