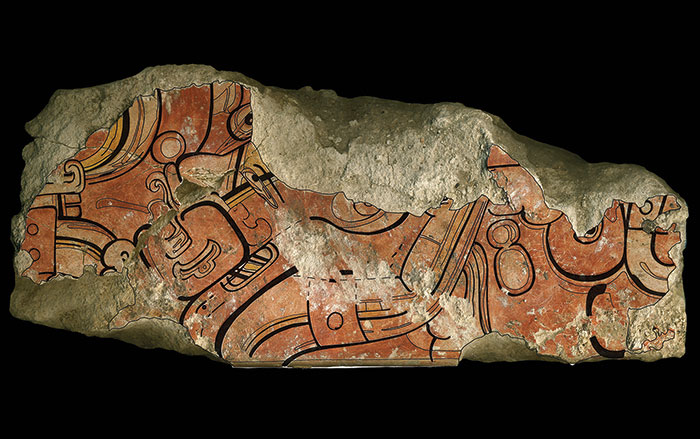
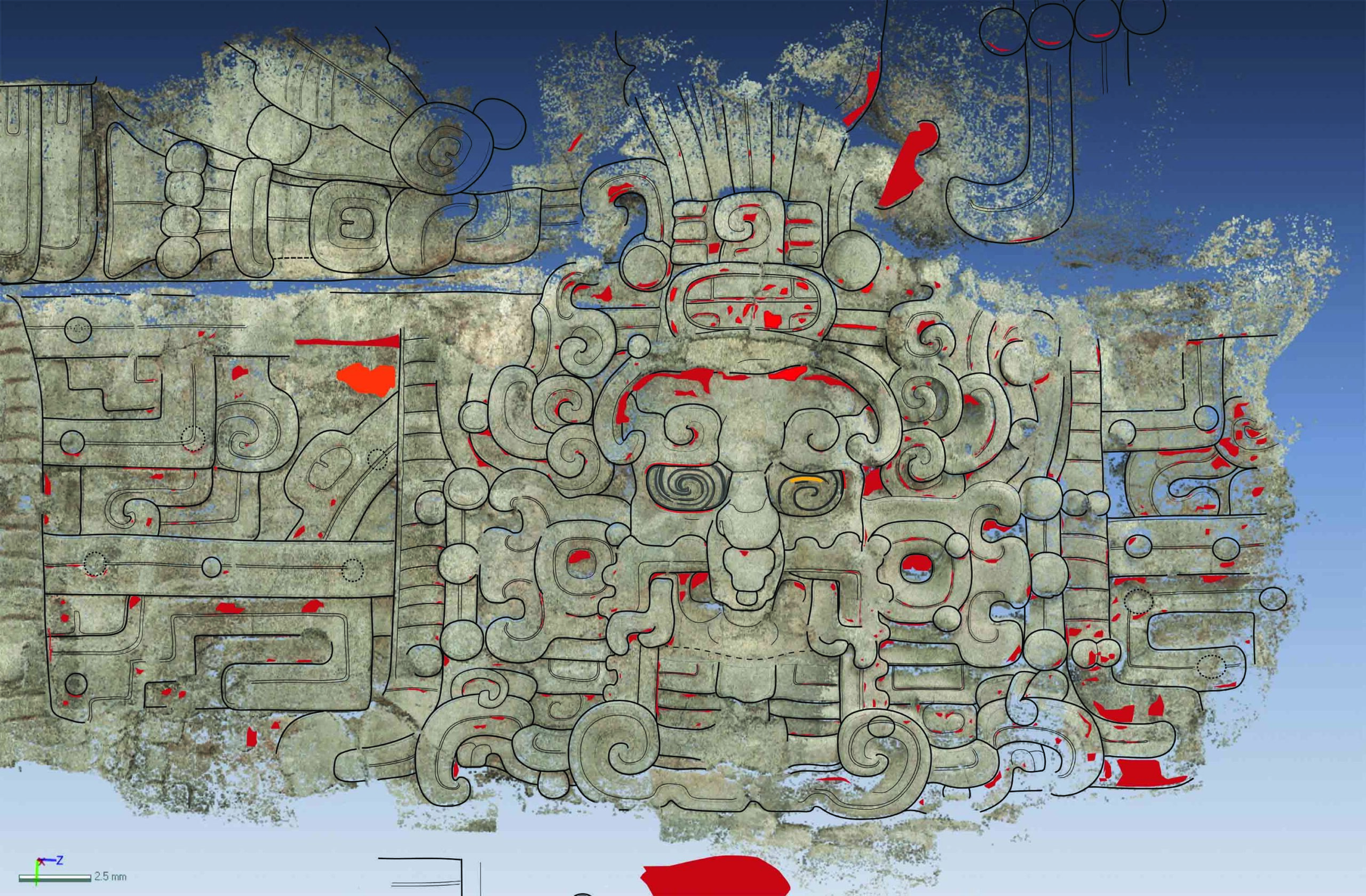
Archaeologists have unearthed a spectacular series of stucco masks at the Maya city of El Zotz. Dating to between A.D. 350 and 400, the five-foot-tall masks decorated a temple atop El Diablo pyramid, which commemorates the founder of the city’s royal dynasty. The masks were painted bright red and depict several deities, including the sun god. They show different phases of the sun as it makes its way across the sky. Between the gods are representations of Venus and other planets. “It’s a celestial symphony,” says Brown University archaeologist Stephen Houston, who co-led the excavation with Edwin Roman of the University of Texas. “The sun is closely associated with Maya kingship, and these images celebrate that link.”