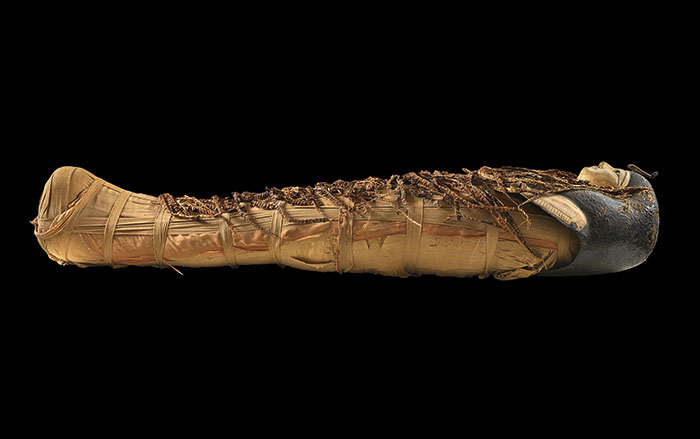
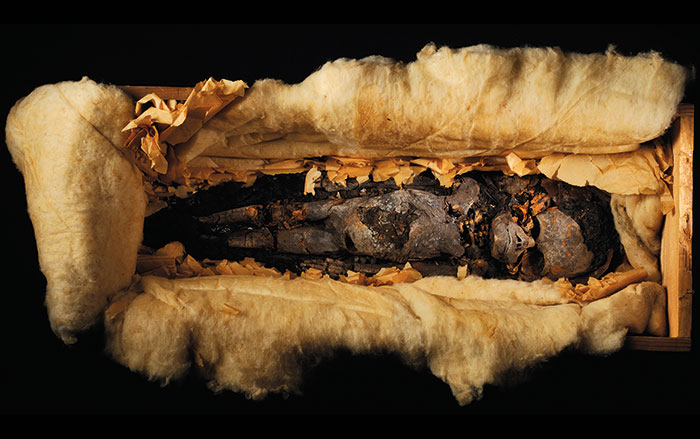
A mummified kestrel’s CT scan shows it choked on its last meal, probably because it had been force-fed. This bird of prey from Egypt, in the collection of Iziko Museums of South Africa in Cape Town, is one of millions of animals mummified as religious offerings, called votive mummies. Kestrels, which are common in Egypt, usually regurgitate the indigestible parts of their meals as pellets. The virtual autopsy of this bird shows that its stomach already contained digested remains from two mice and a sparrow, some of which it would have regurgitated before it consumed yet another mouse. The tail of that last meal got stuck in the gullet and choked the bird. Ancient Egyptians often force-fed their captive animals, which makes this the earliest known evidence of keeping and possibly breeding raptors.