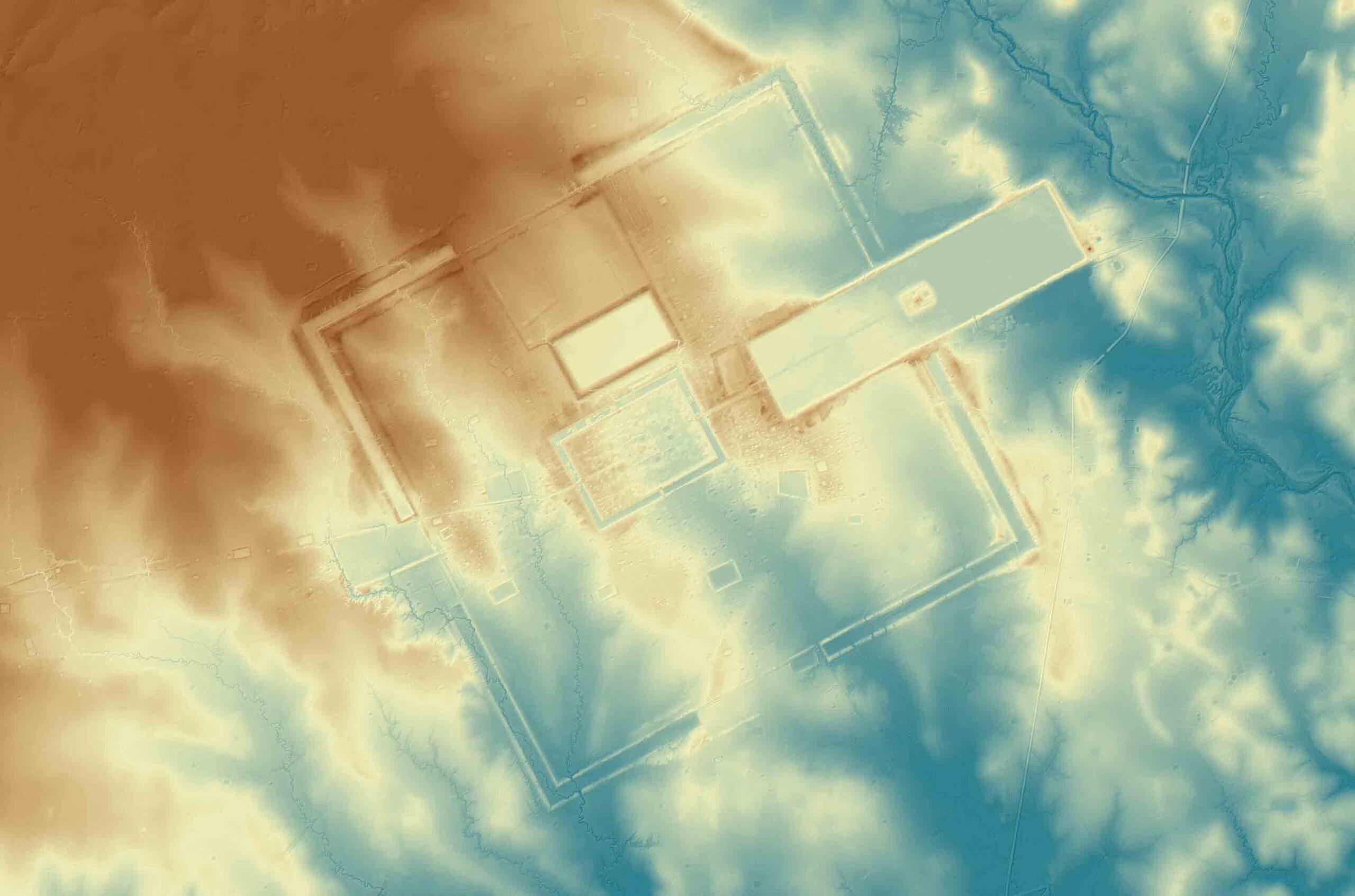
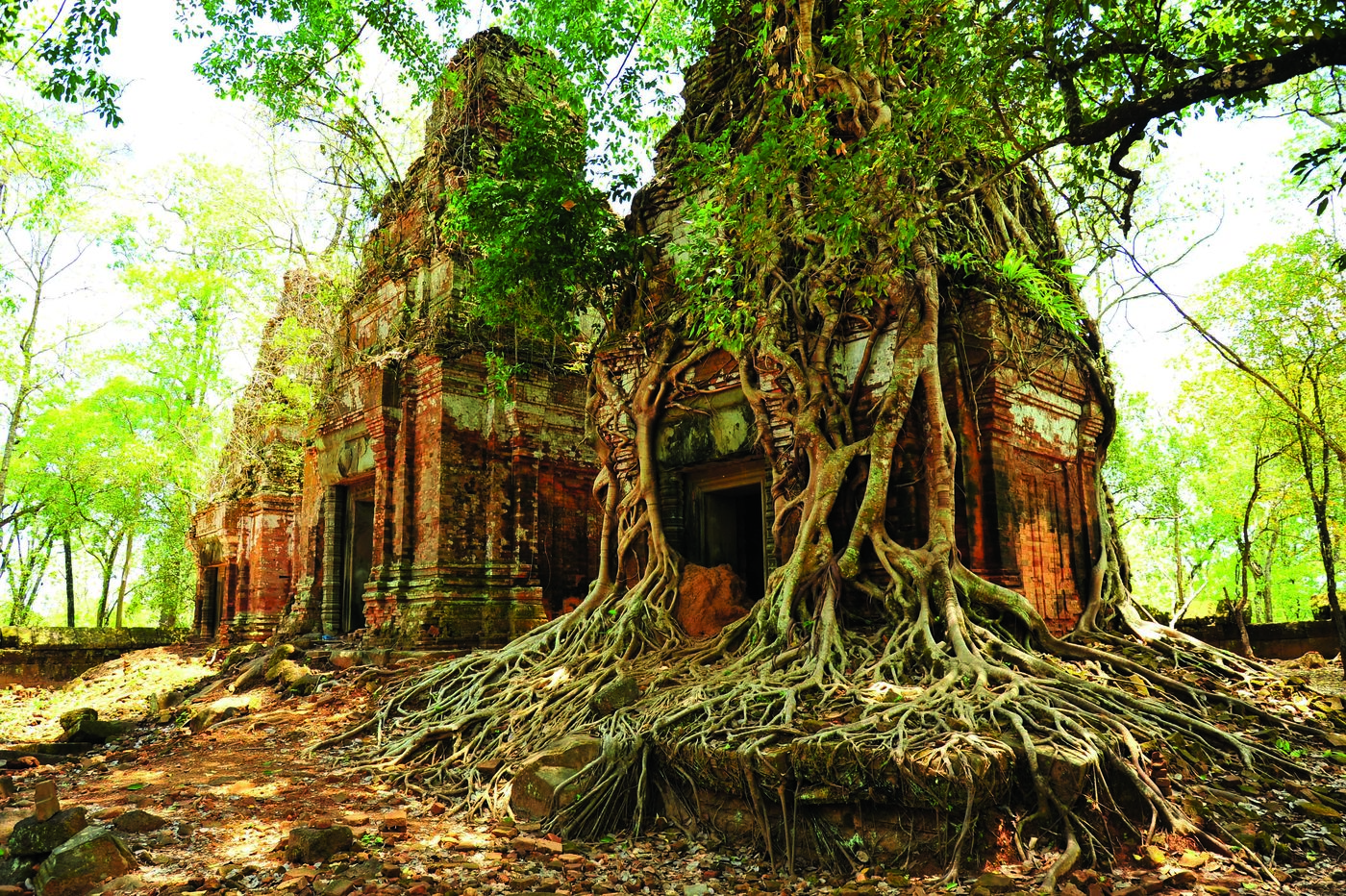
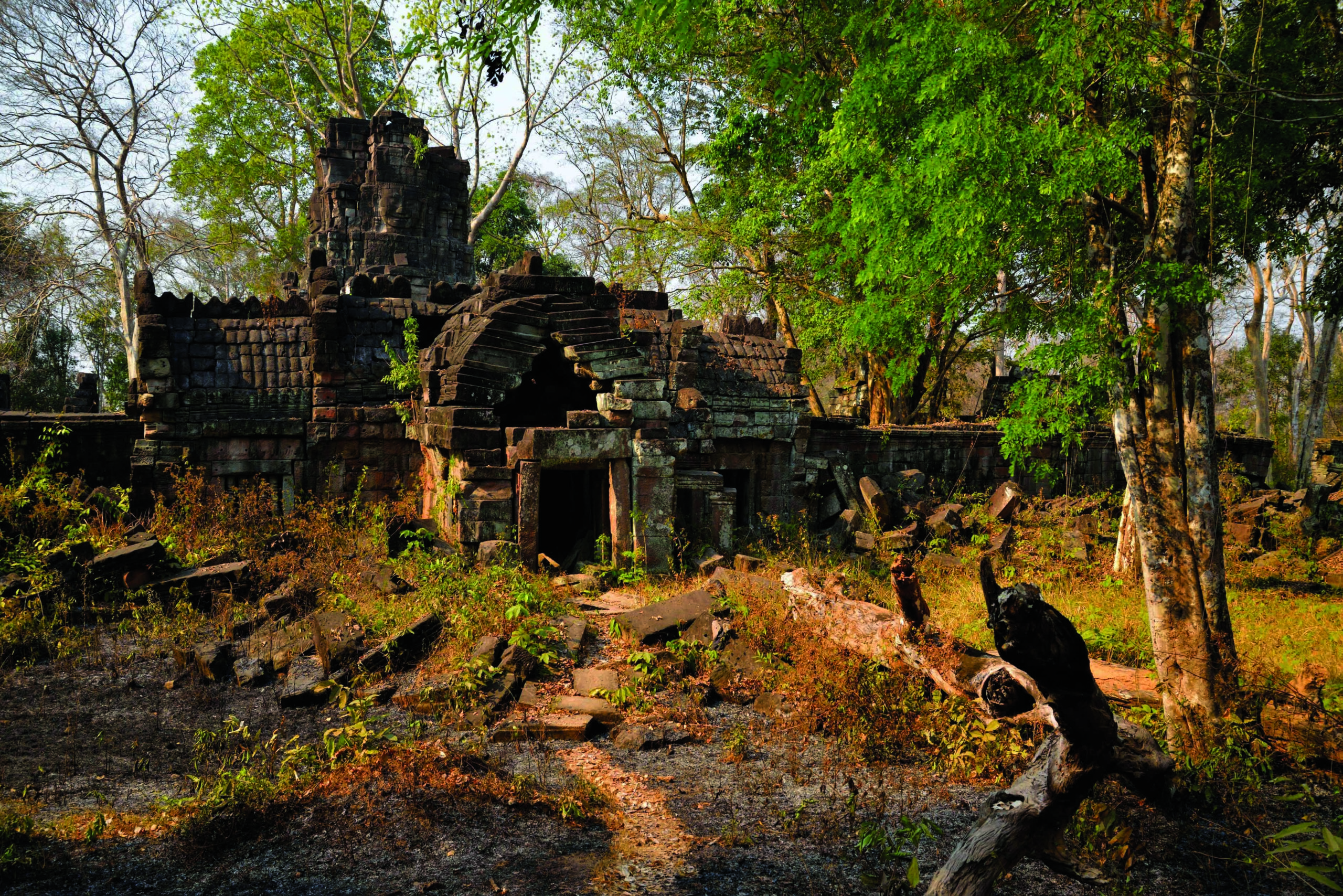
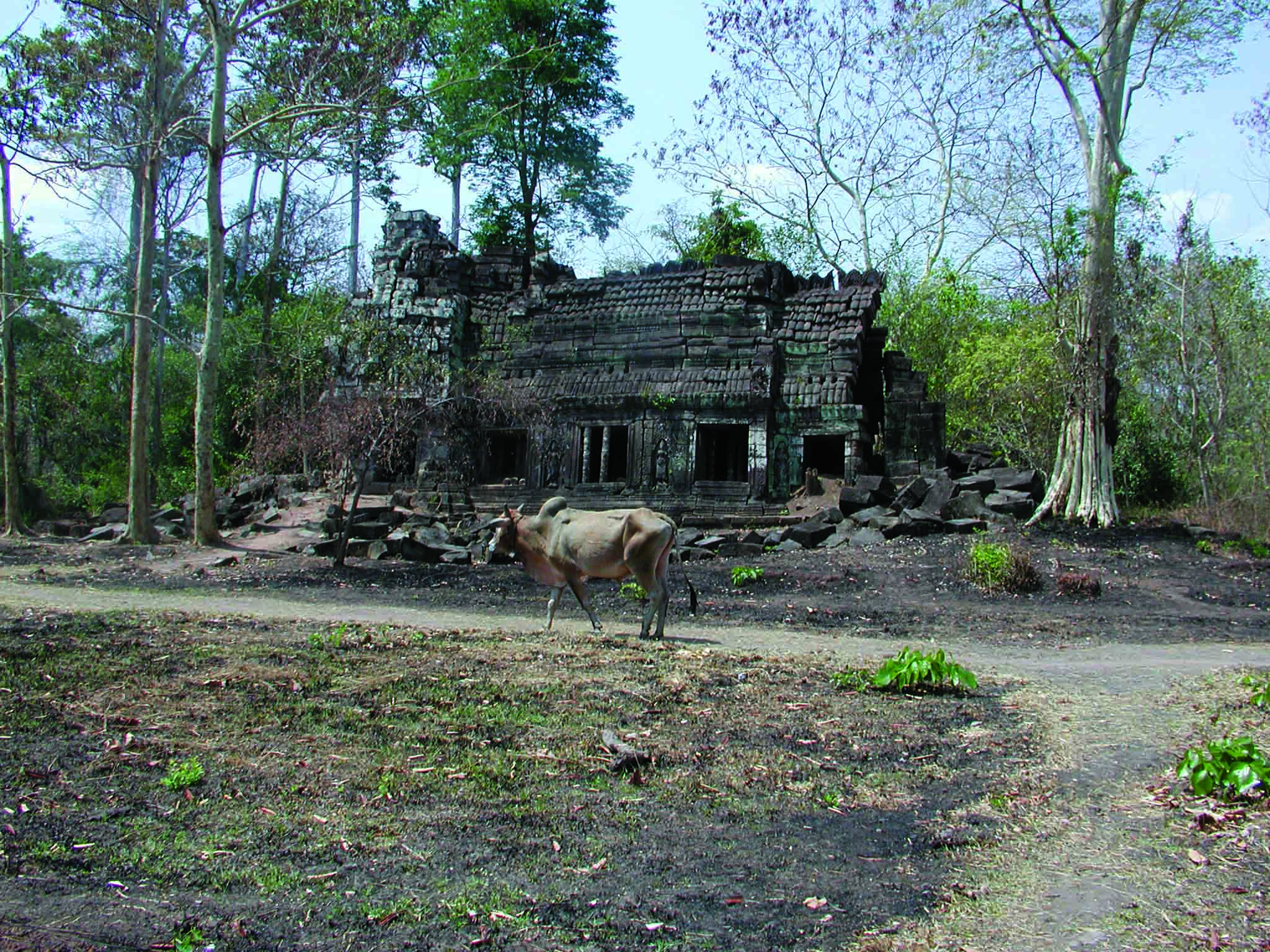
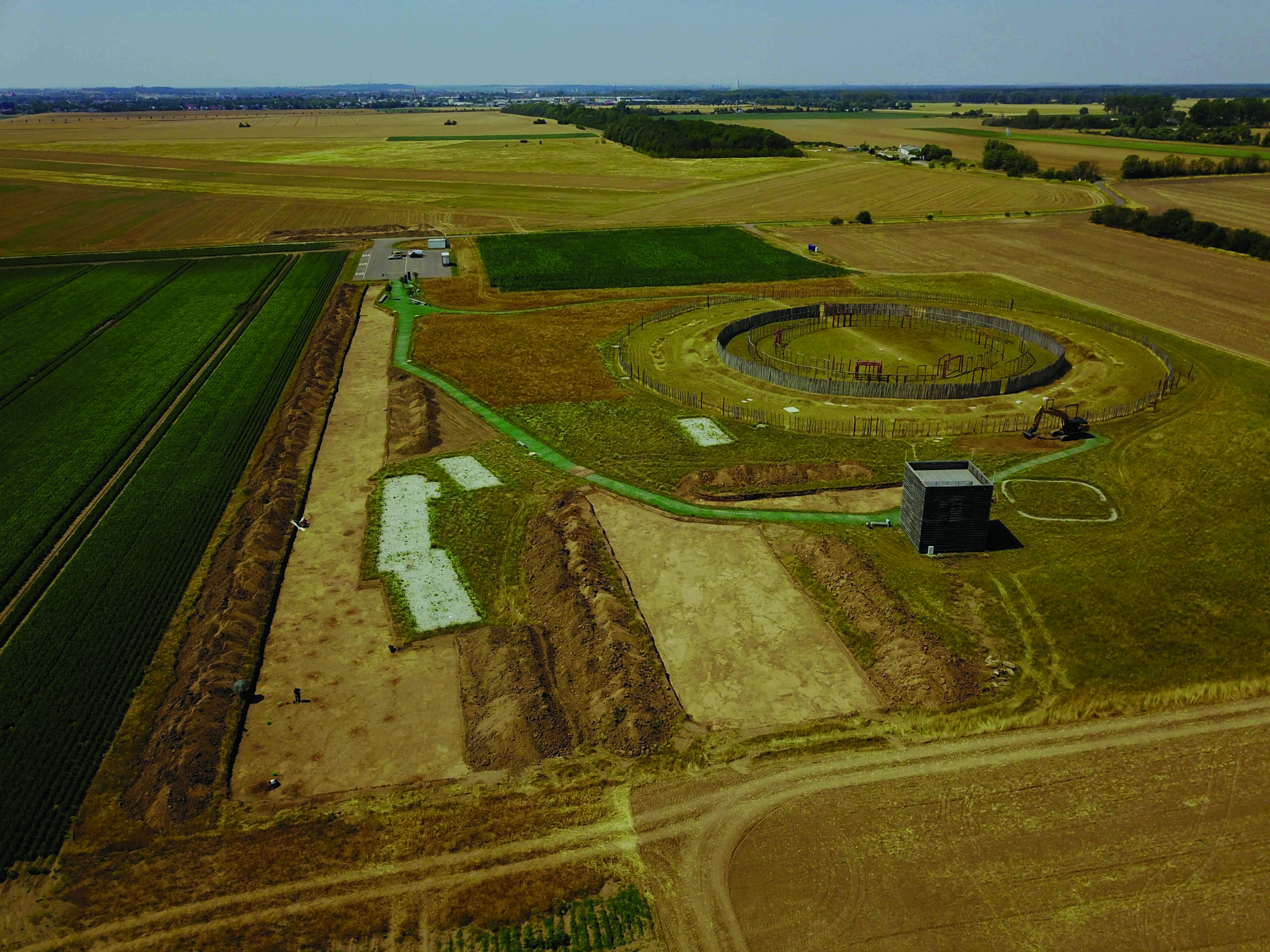
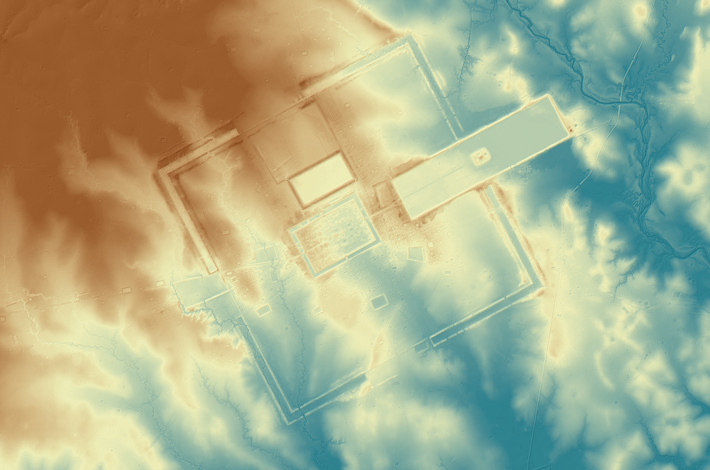
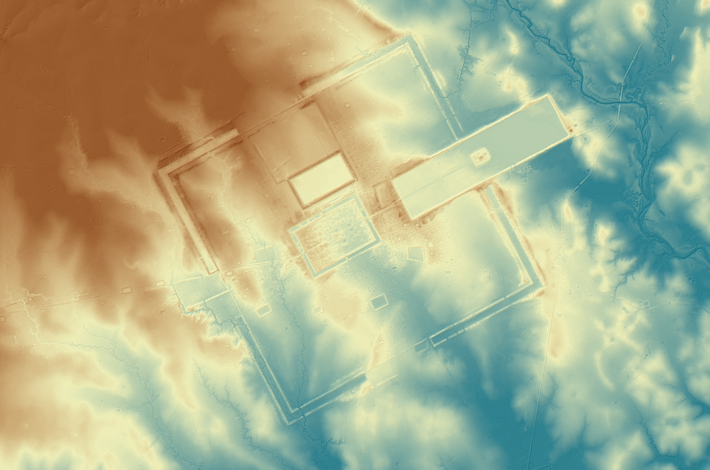
The countryside surrounding the Khmer Empire’s capital of Angkor is blanketed with thick jungle, which has hindered archaeological investigation for more than a century. However, laser scanning technology was finally able to do what researchers couldn’t and peer through the dense vegetation, revealing unknown urban settlements and hundreds of hidden archaeological features. “Had you been there a thousand years ago, the forest wouldn’t have existed,” says Damian Evans of the French School of Asian Studies. “You would have seen a vast, bustling metropolis of wooden dwellings and fields stretching off in every direction.” The 3-D images captured in 2015 were the result of the most extensive archaeological scanning project ever undertaken. Evans’ team surveyed 737 square miles of terrain at the heart of the Khmer Empire, which flourished between the ninth and fifteenth centuries. The images captured a complex system of roads, canals, and dams that attest to the civilization’s scale, sophistication, and remarkable ability to engineer Cambodia’s challenging landscape.