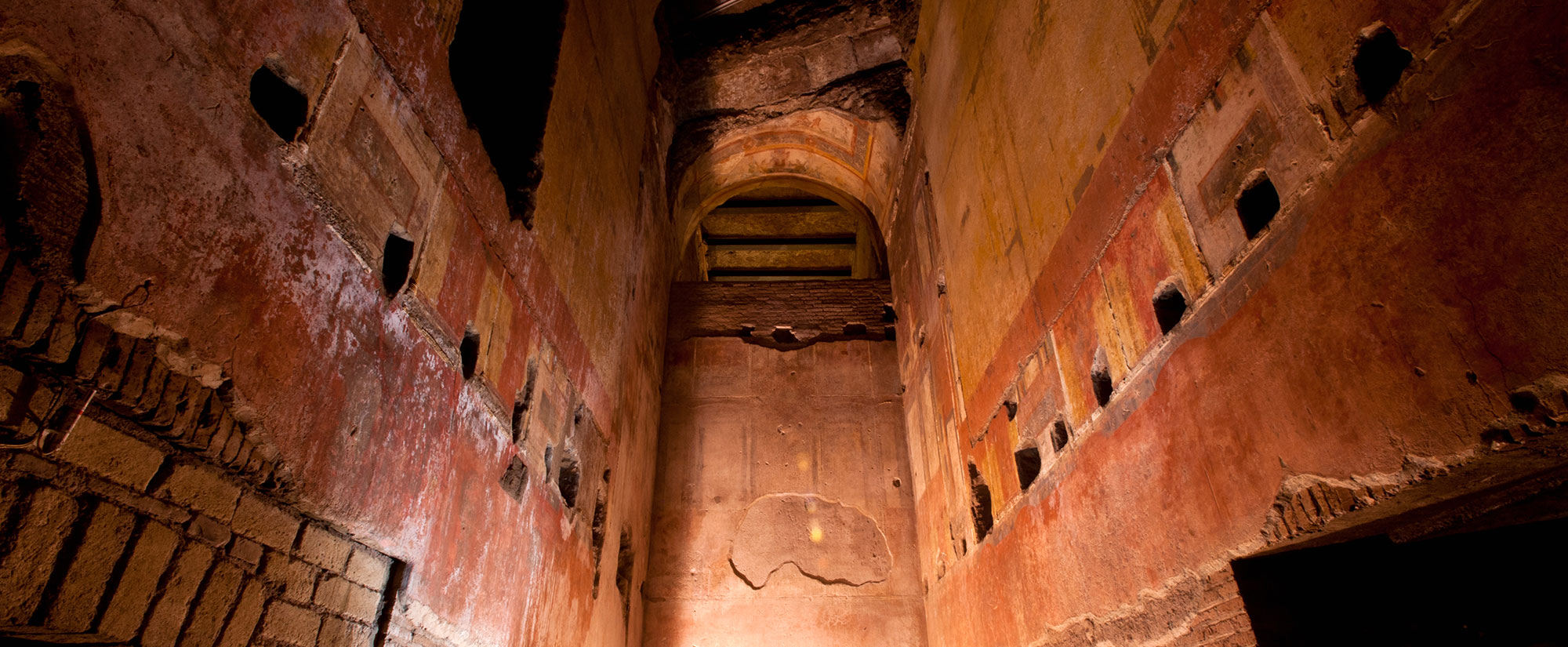
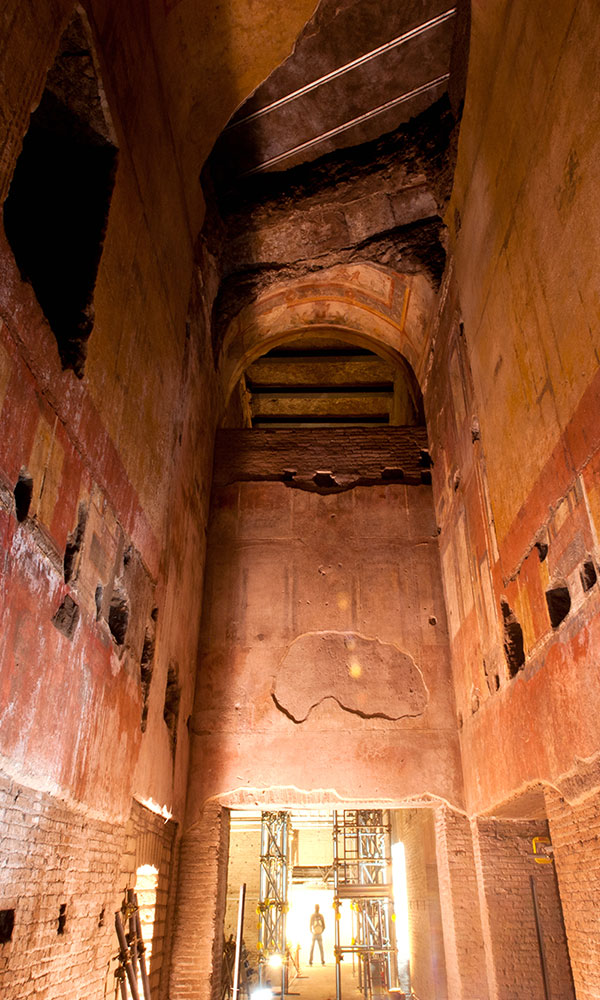
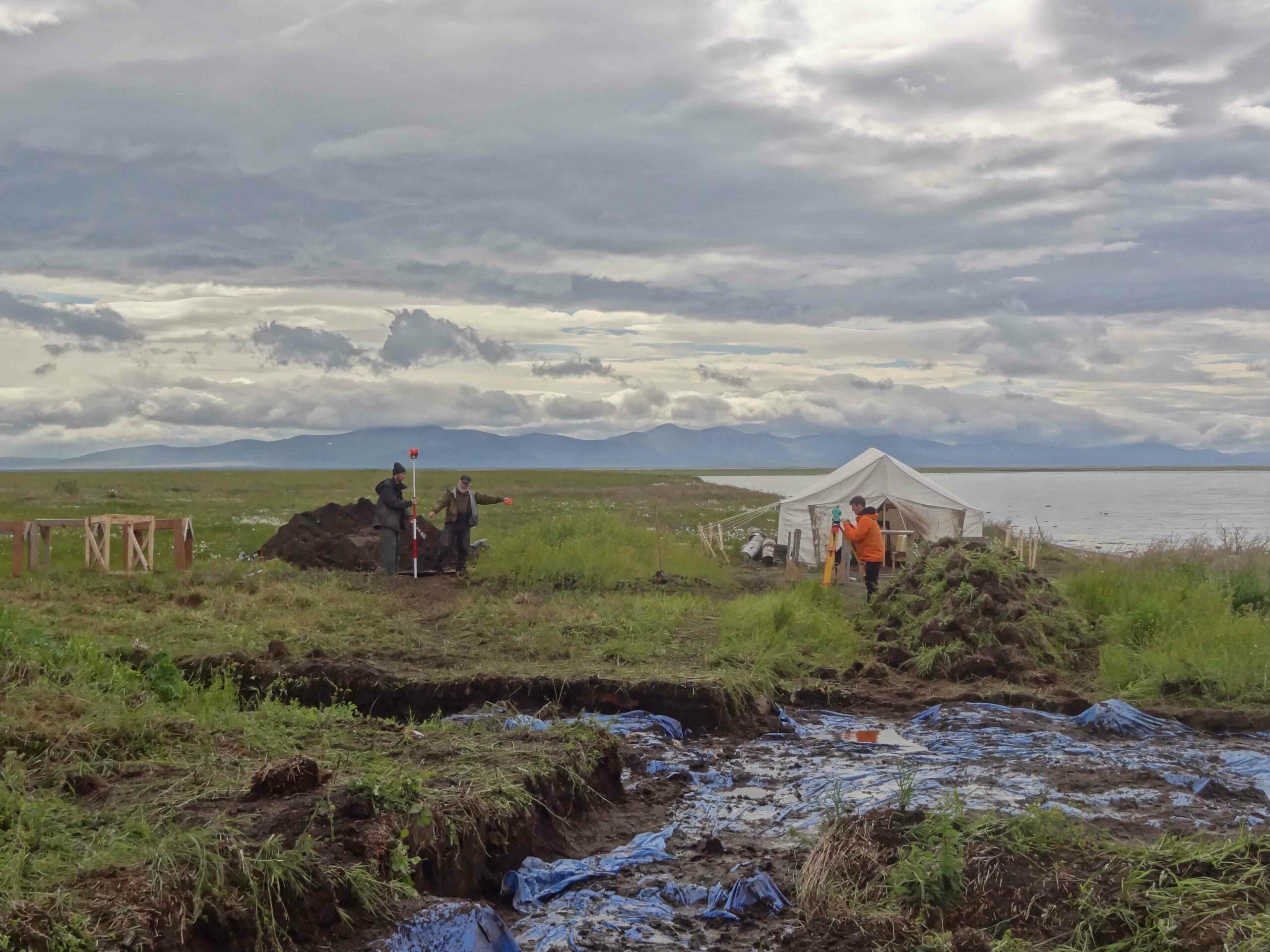
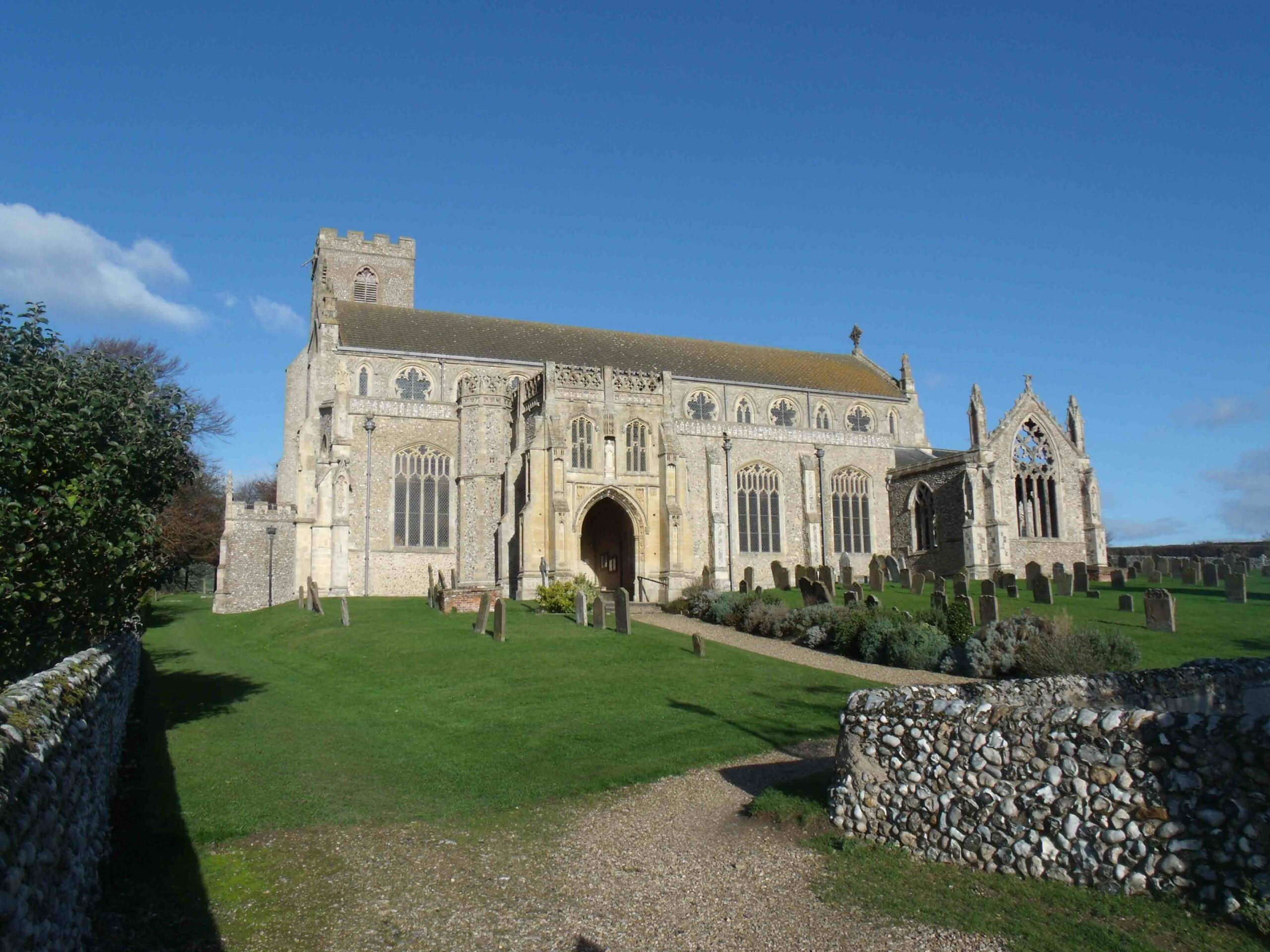
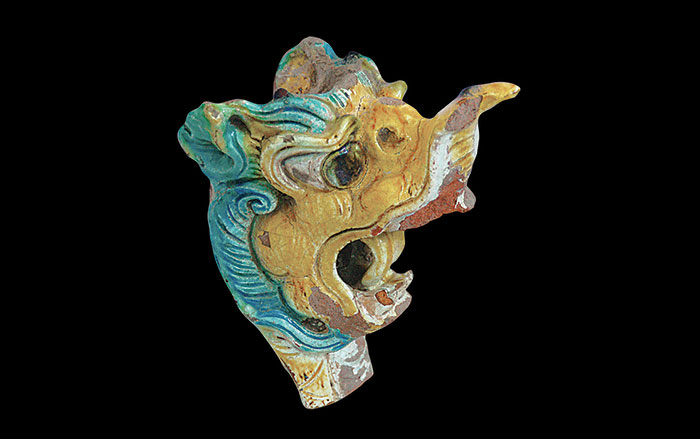
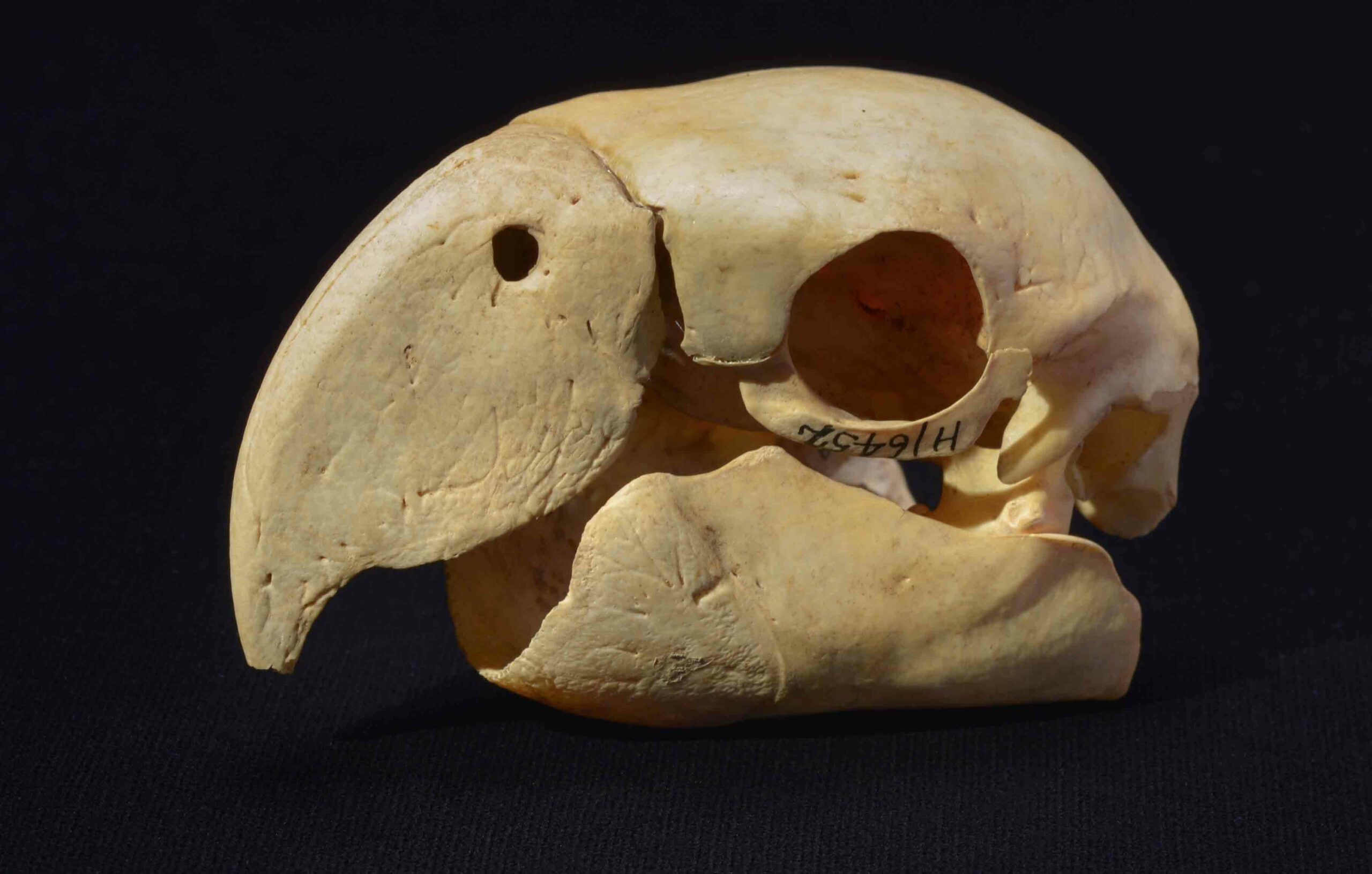
In the prehistoric American Southwest, trade with distant Mesoamerica was a source of power and prestige that could make or break a ruler. Within the massive multistory buildings at New Mexico’s Chaco Canyon, for instance, archaeologists have discovered exotic goods from Mexico, such as cacao and the remains of 33 scarlet macaws, whose natural habitat is 1,000 miles away on the Gulf of Mexico. Scholars had assumed that long-distance trade became important only during the period when Chaco’s power was greatest, from A.D. 1040 to 1110. But now a team has dated the macaw bones and found that some were imported as early as A.D. 900.
“I was very much surprised,” says American Museum of Natural History archaeologist Adam Watson, who helped organize the dating. “I, along with everyone else, assumed the trade networks with Mexico didn’t become important until Chaco expanded. Now we have evidence that control over trade and political power were being consolidated long before then.”