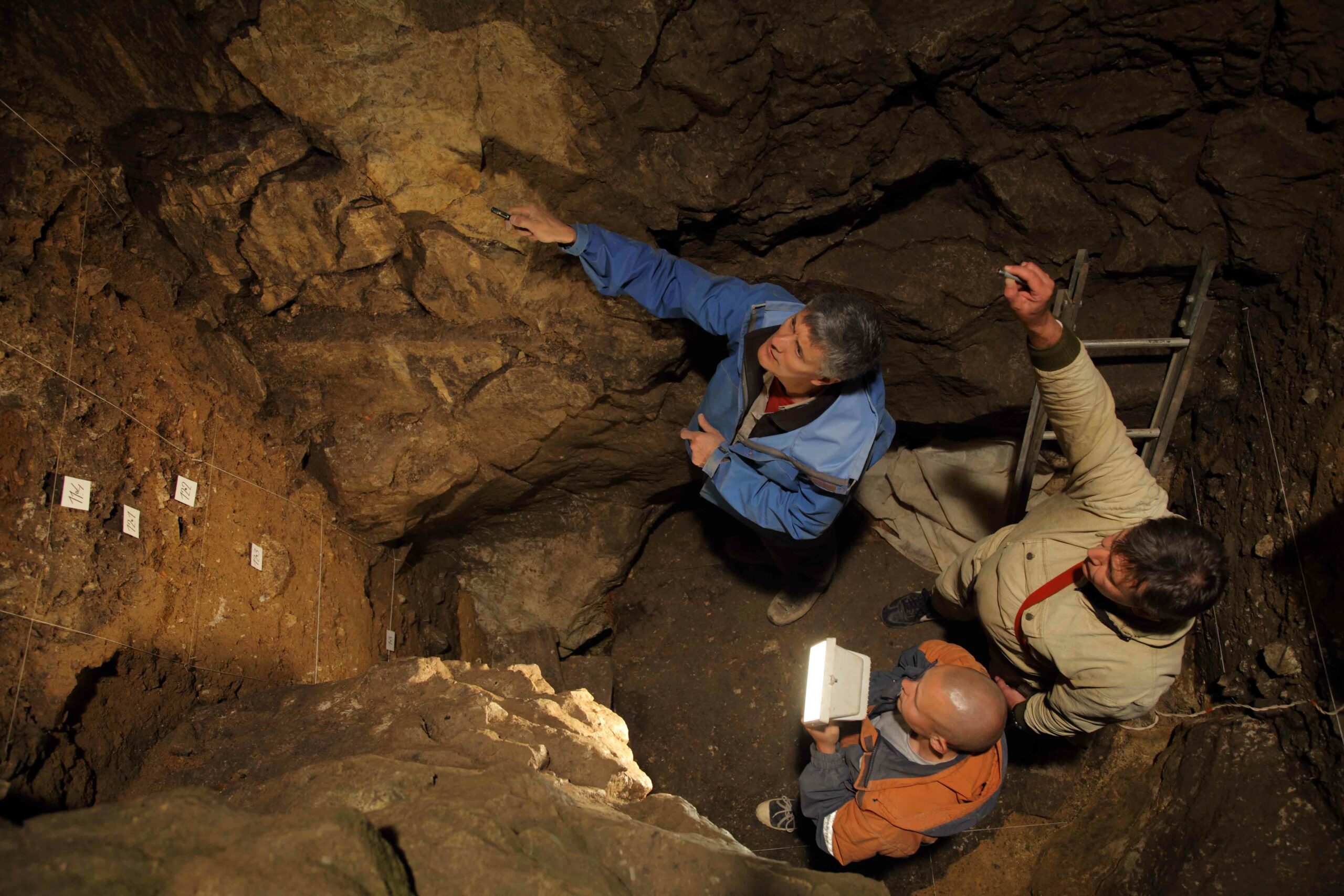
LEIPZIG, GERMANY—Neanderthal nuclear DNA has been recovered from sediments collected in one cave in northern Spain and two caves in Siberia’s Altai Mountains by a team of researchers led by Benjamin Vernot of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, according to a Cosmos Magazine report. DNA is left behind by skin flakes, hair, excrement, sweat, and blood. Previous analysis of soil samples has detected ancient hominin mitochondrial DNA, which occurs in greater volume in a cell than nuclear DNA, but it is inherited from the mother alone and is used to create energy, and therefore offers less information about an individual than nuclear DNA, which is inherited from both parents and carries information for making all of the proteins in the body. Vernot and his colleagues sorted the DNA of other animals out of the more than 150 soil samples and found chromosomes from multiple Neanderthal individuals. The study revealed that inhabitants of Russia’s Chagyrskaya Cave belonged to one population who lived there for a short period of time. Their chromosomal DNA resembled that obtained from a fossil found in the cave, explained Kseniya Kolobova of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Two separate populations, one dated to about 135,000 years ago, and the other dated to about 105,000 years ago, inhabited Spain’s Galería de las Estatuas. The later wave of Neanderthals is thought to have replaced the earlier one. To read about a 2010 study that successfully sequenced a Neanderthal genome for the first time, go to "Neanderthal Genome," one of ARCHAEOLOGY's Top 10 Discoveries of the Decade.