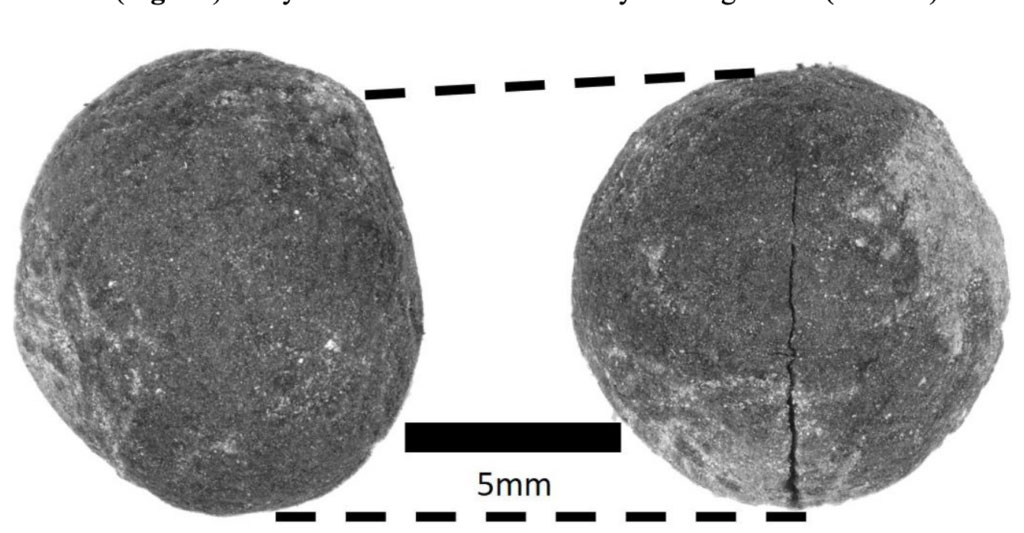
ST. LOUIS, MISSOURI—According to a statement released by Washington University in St. Louis, an excavation in Kenya’s Kakapel Rockshelter has uncovered evidence of the types of crops grown by East Africa’s early farmers. The plant remains were recovered from a hearth at the rock shelter, which was first occupied more than 9,000 years ago. “We found a huge assemblage of plants, including a lot of crop remains,” said Natalie Mueller of Washington University. For example, the 2,300-year-old cowpeas, or black-eyed peas, recovered from the hearth are thought to have originated in West Africa and traveled to East Africa with Bantu-speaking peoples from Central Africa. The presence of this crop in the rock shelter reflects interactions between East Africa’s local herders and incoming Bantu-speaking farmers, explained Emmanuel Ndiema of the National Museums of Kenya. In addition, the study suggests that sorghum from northeastern Africa was introduced to East Africa about 1,000 years ago, when local millet was also cultivated. Field peas, a crop grown in Egypt, may have come to East Africa down the Nile River and through Sudan, but the sample may be an Abyssinian pea, which had been domesticated independently in Ethiopia, the researchers added. “Our work shows that African farming was constantly changing as people migrated, adopted new crops, and abandoned others at a local level,” Mueller concluded. Read the original scholarly article about this research in Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. To read about ancient cultivation of millet and other crops in northern China, go to "The Ancient Promise of Water: Like Water for Wheat."