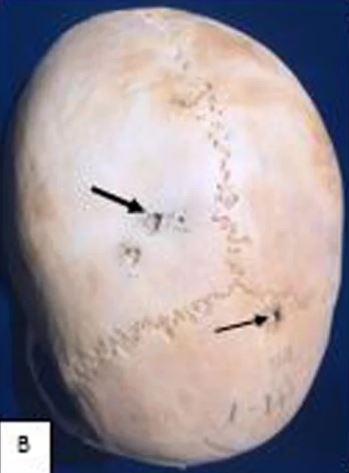
ONTARIO, CANADA—According to a report in Live Science, retired anthropologist El Molto of the University of Western Ontario and physician Peter Sheldrick studied the prevalence of cancer in the ancient Egyptian population of more than 1,000 people buried in the Dakhleh Oasis between 1,500 and 3,000 years ago. The researchers detected just six cases of cancer through lesions and bone damage on the skeletons, including a toddler who had leukemia, and a man in his 50s whose rectal cancer tumor was preserved in his mummified remains. A woman who had a hole in her hip bone measuring about 2.5 inches is also thought to have suffered from a tumor, but scientists are not able to determine where the disease originated in her body. Three people—two women and one man—who died in their 20s or 30s are also thought to have succumbed to cancer. Molto and Sheldrick suggest they were infected with human papillomavirus (HPV), an ancient virus known to cause cancer in young people. The study suggests the rate of cancer was much lower than it is today, even though some of the ancient Egyptians buried in the Dakhleh Oasis may have had cancer without it having left marks on their bones. For more on cancer in the archaeological record, go to “Ancient Oncology.”










