MUNICH, GERMANY—New Scientist reports that Egyptians living some 3,500 years ago may have eaten watermelons similar to those we enjoy today. Botanists Susanne Renner of the University of Munich and Guillaume Chomicki of the University of Oxford analyzed a tiny piece of one of the ancient watermelon leaves that were discovered in an Egyptian tomb and sent to botanist Joseph Hooker in London in the late nineteenth century. Fortunately, the partial genome sequence the researchers obtained from the artifact contained genes related to color and taste. This melon plant did not produce the bitter cucurbitacins found in Africa’s wild, round watermelons. It also lacked a functioning gene for transforming the red pigment lycopene into another substance, which means the plant produced fruit with red flesh. Ancient Egyptian images of watermelons depict them with an elongated shape, but the partial gene sequence did not reveal the contours of this particular plant's fruit. Renner said the analysis also suggests the plant was related to sweet watermelons with white flesh that are grown to this day in Sudan. To read about another recent discovery in Egypt, go to “Family Secrets.”
Ancient Egyptians Enjoyed Sweet Watermelons
News May 21, 2019
SHARE:
Recommended Articles
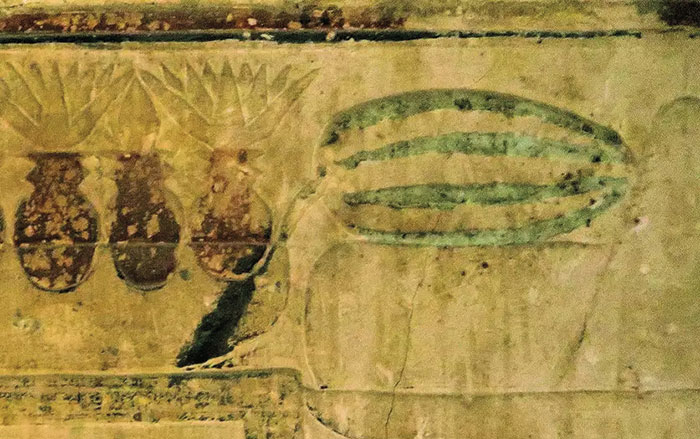

Courtesy Susanne Renner
Digs & Discoveries May/June 2025
The Cat and the Fat

SMB - Ägyptisches Museum und Papyrussammlung/Photo: Sandra Steiß
Digs & Discoveries May/June 2025
Pharaoh's Fate

© Zahi Hawass
Digs & Discoveries March/April 2025
Primordial Alphabet Soup
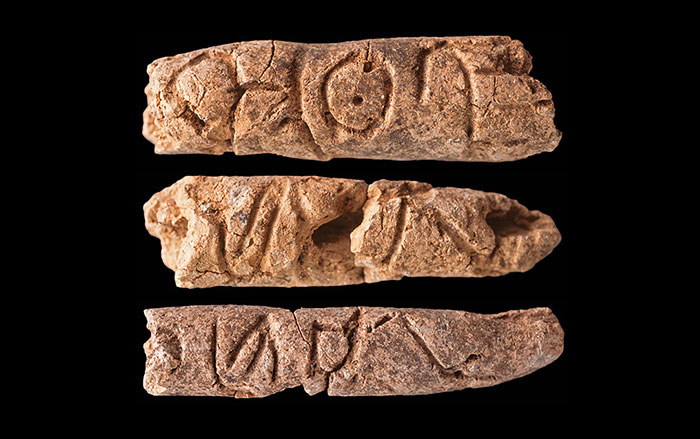

Courtesy Glenn Schwartz
-
Features March/April 2019
Sicily's Lost Theater
Archaeologists resume the search for the home of drama in a majestic Greek sanctuary
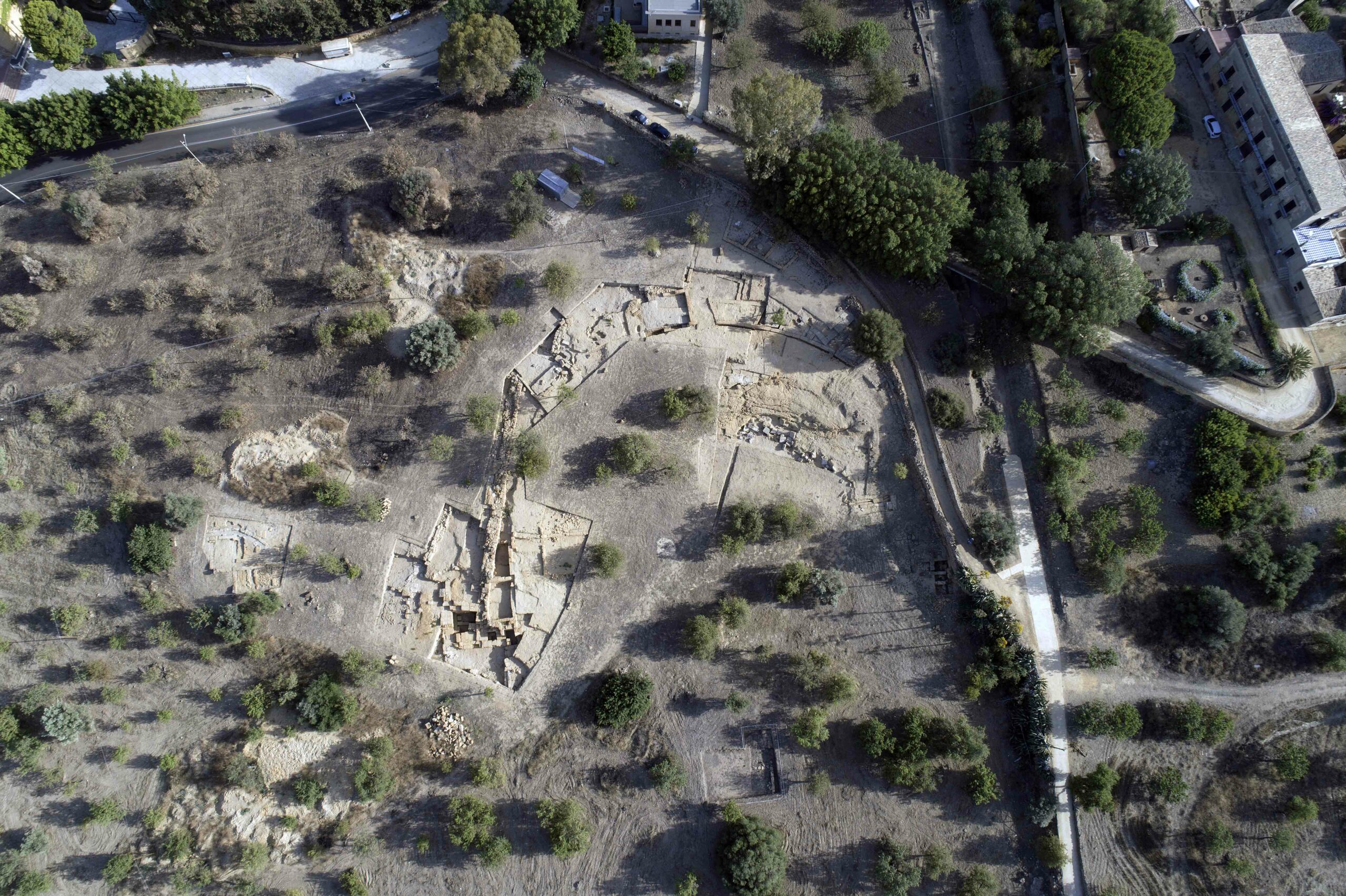 (Giuseppe Cavaleri)
(Giuseppe Cavaleri) -
Letter From Texas March/April 2019
On the Range
Excavations at a ranch in the southern High Plains show how generations of people adapted to an iconic Western landscape
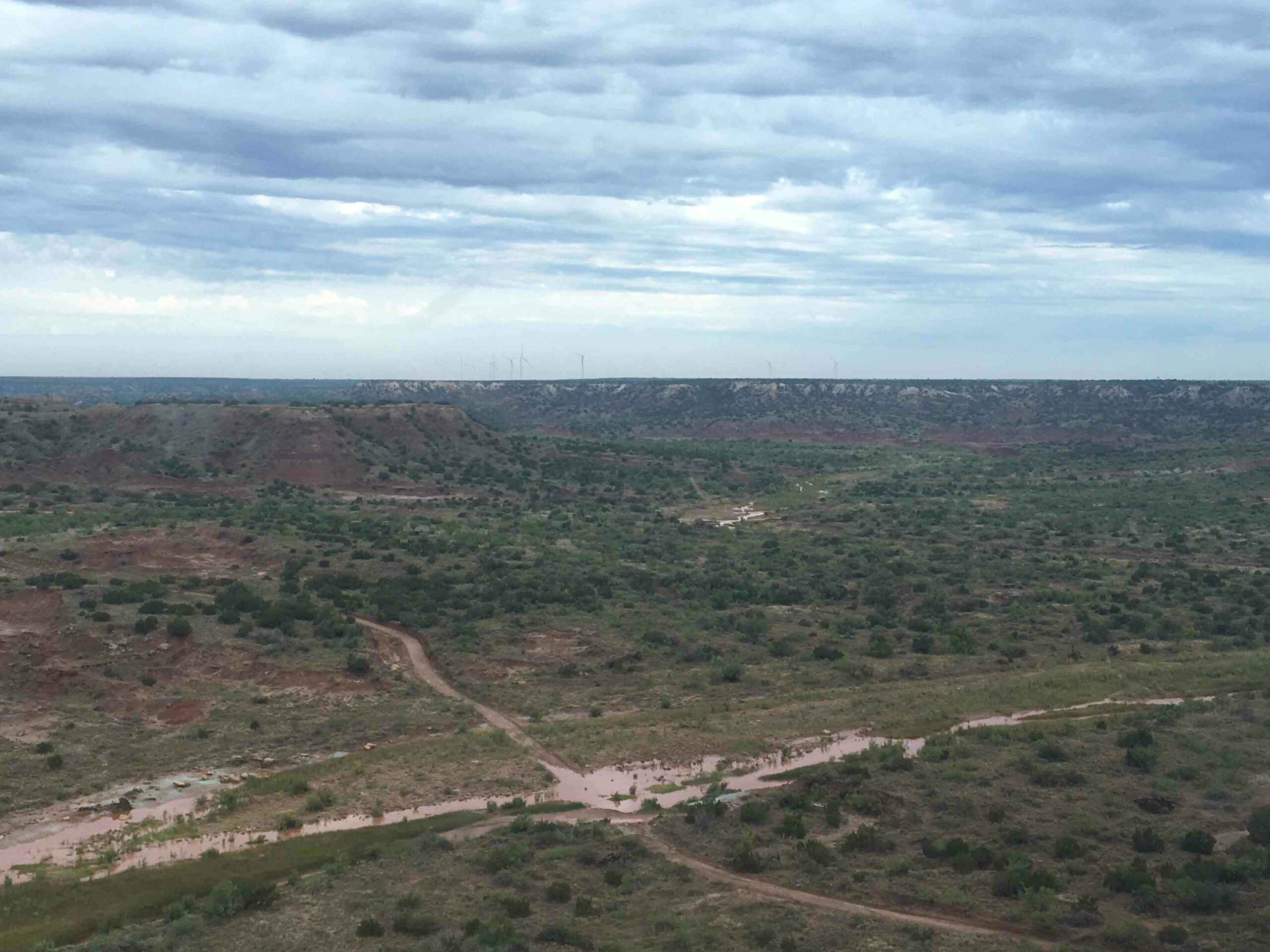 (Eric A. Powell)
(Eric A. Powell) -
Artifacts March/April 2019
Medieval Seal Stamp
 (Rikke Caroline Olsen/The National Museum of Denmark)
(Rikke Caroline Olsen/The National Museum of Denmark) -
Digs & Discoveries March/April 2019
Fairfield's Rebirth in 3-D
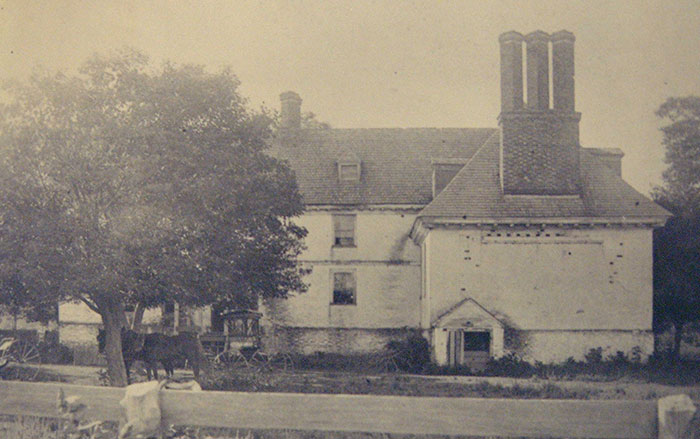 (Virginia Department of Historic Resources)
(Virginia Department of Historic Resources)