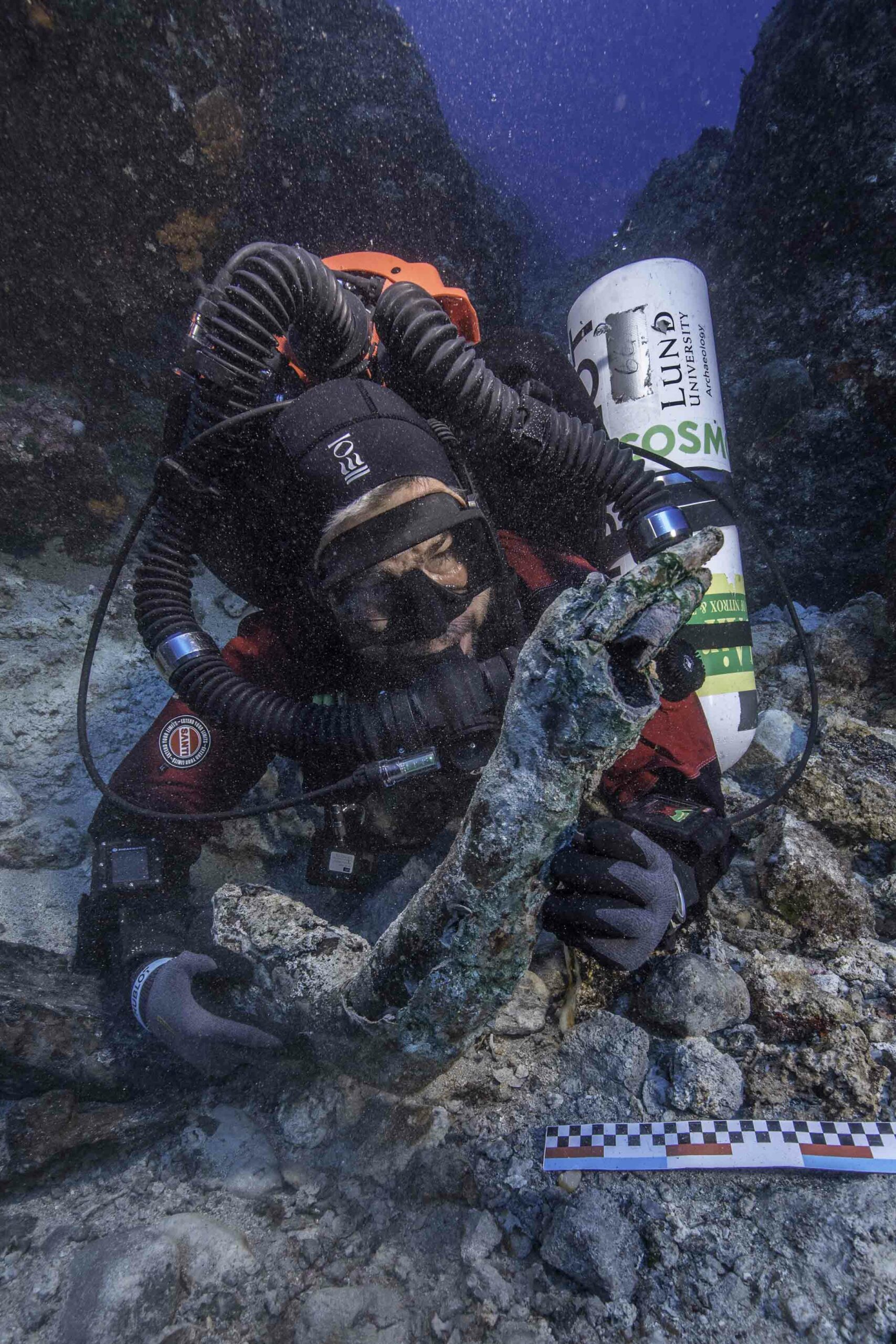
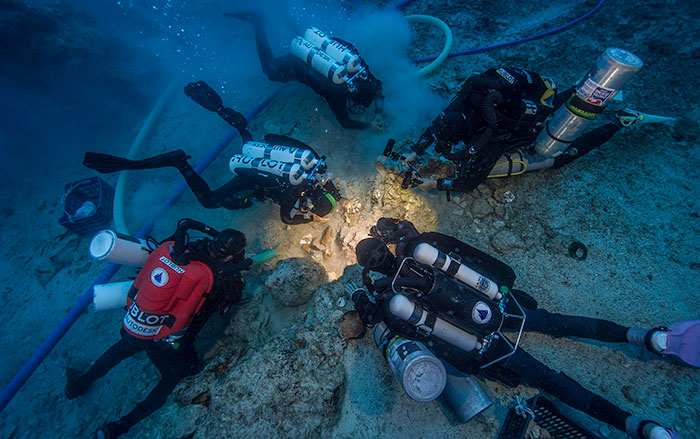
ATHENS, GREECE—Using X-ray scanning equipment and imaging technology, an international team of scientists has read most of the explanatory text engraved in tiny letters on the known surviving fragments of the Antikythera Mechanism. Mike Edmunds of Cardiff University said that the text does not instruct the reader on the use of the device, but is more like a descriptive label. The artifact, recovered from a first-century B.C. shipwreck off the coast of a Greek island in the early years of the twentieth century, is made up of bronze gears and plates, and was probably encased in wood and operated with a hand crank. It is thought to have functioned as an astronomical instrument to track the position of the sun, the phases of the moon, the positions of the planets, and the timing of eclipses. “It’s like a textbook of astronomy as it was understood then, which connected the movements of the sky and the planets with the lives of the ancient Greeks and their environment,” Alexander Jones of New York University said in an Associated Press report. Investigators have returned to the shipwreck to look for more pieces of the device. For more on archaeology in Greece, go to "The Acropolis of Athens."