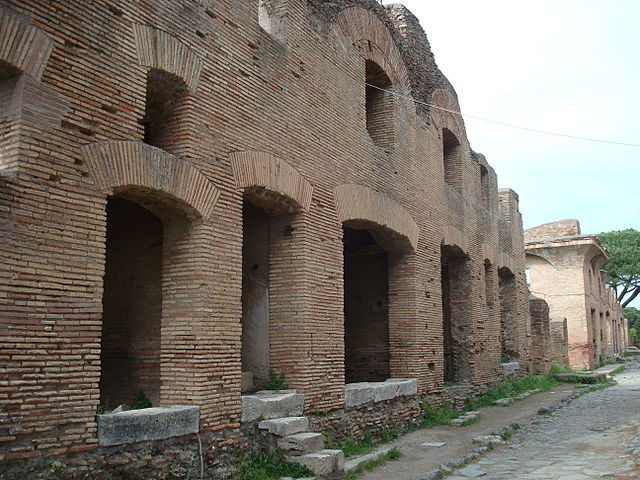
HAMILTON, ONTARIO—CNN reports that researchers from McMaster University, Historic England, and the English Heritage Trust examined the remains of children who had been buried in cemeteries ranging from northern England to southern Spain and were surprised to find that more than one in 20 of those who lived between the first and sixth centuries A.D. showed signs of rickets, or weakened bones caused by vitamin D deficiency. The scientists suggest the disease may have resulted from the weaker sunshine in northern Europe, which can make it harder for the body to absorb vitamin D, and the fact that parents in the northern parts of the Roman Empire probably kept their children inside more of the time in an effort to protect them from the cool, cloudy climate. Children who lived near the Mediterranean Sea would have likely been exposed to more sunshine throughout the year, which would have helped to strengthen their bones, unless they lived in crowded apartment buildings, such as those found in the Rome’s seaport of Ostia. Megan Brickley of McMaster University said the small windows, closed-in courtyards, and narrow streets found there could account for the cases of rickets detected in Ostia’s ancient cemetery. For more on the detection of medical problems in ancient remains, go to “Heart Attack of the Mummies.”