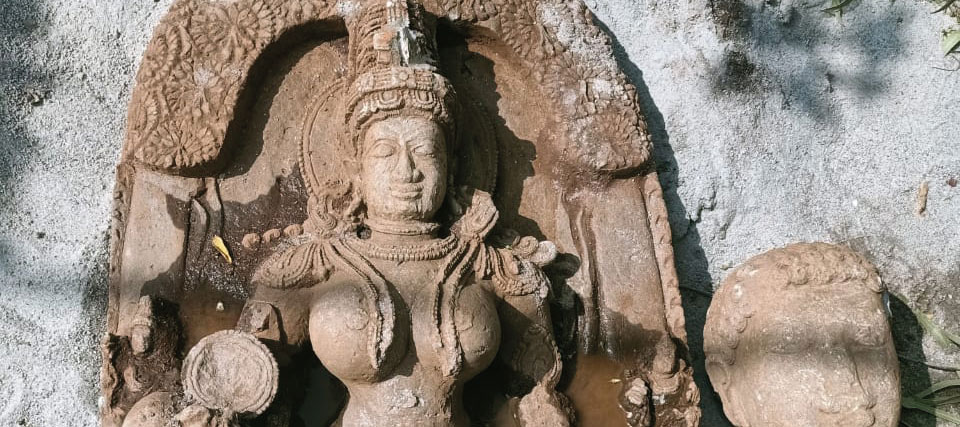
INDIA: Many studies have looked at bioturbation—how plants and animals alter archaeological sites—but rarely in ground saturated by monsoons. Researchers working on Paleolithic sites noticed that water buffalo leave deep, lasting footprints in mud. So they set up an experiment, creating and placing their own stone tools, wetting the ground, and leading buffalo across it. They found the hooves could push artifacts down by eight inches—thousands of years in the archaeological record in some places—and noted patterns that can help determine if other sites have been disturbed by lumbering bovines.