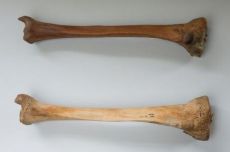
LONDON, ENGLAND—Raman spectroscopy, a non-destructive laser technology, has been used to analyze leg bones of sailors who died on King Henry VIII’s flagship, the Mary Rose, which sank in battle on July 19, 1545. The tests were conducted at the Royal National Orthopedic Hospital, as part of a study by a team from University College London, the Science and Technology Facilities Council, and The Mary Rose Trust. Some of the bones appeared anatomically healthy, and some were abnormal in shape. The results of the testing confirmed that the abnormal bones also had chemical abnormalities, perhaps caused by rickets, a metabolic bone disease caused by deficiencies in the diet. “This is the first time that this laser technology has been used to study bone disease in archaeological human bone. We have identified chemical changes in the bones, without damaging them. There is strong evidence to suggest that many of the sailors had suffered from childhood rickets and we hope to apply the Raman technique to the study of modern day rickets,” said Dr. Jemma Kerns, RAMAN Clinical Study Manager at University College London and the Royal National Orthopedic Hospital. To read more about the Mary Rose, see "History's Top 10 Greatest Shipwrecks."










