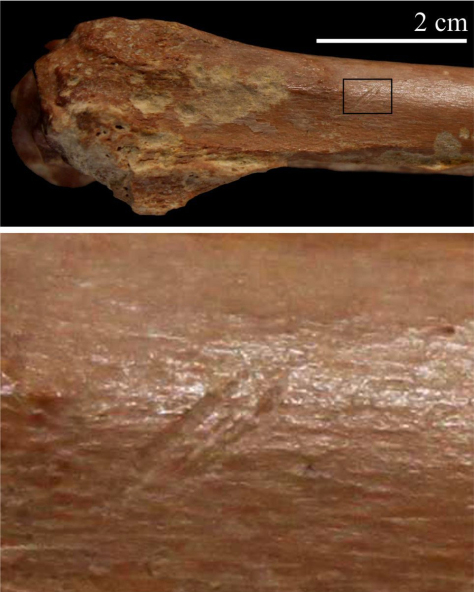
BURGOS, SPAIN—Science News reports that stone tools unearthed in Algeria amid butchered animal bones suggest the evolution of human ancestors was not limited to East Africa. Mohamed Sahnouni of Spain’s National Research Center for Human Evolution and his colleagues say meat-chopping tools found in North Africa were made about 2.4 million years ago, or about 200,000 years more recently than the oldest known tools in East Africa. The scientists think the tools could have been crafted by descendants of East African toolmakers who migrated into North Africa, or they may have been created independently. The animal bones came from savanna-dwellers such as elephants, horses, rhinoceroses, antelopes, and crocodiles that may have been hunted or scavenged from carnovores’ fresh kill sites, Sahnouni said. No hominin remains were found with the tools, so the researchers are not sure who made them. To read about early remains of modern humans discovered in Morocco, go to “Homo sapiens, Earlier Still.”