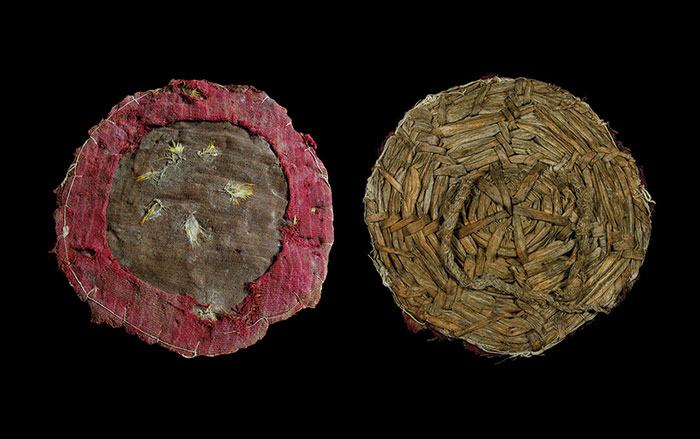
Culture: Pazyryk
Location: Russia
Date: Fourth to Third centuries B.C.
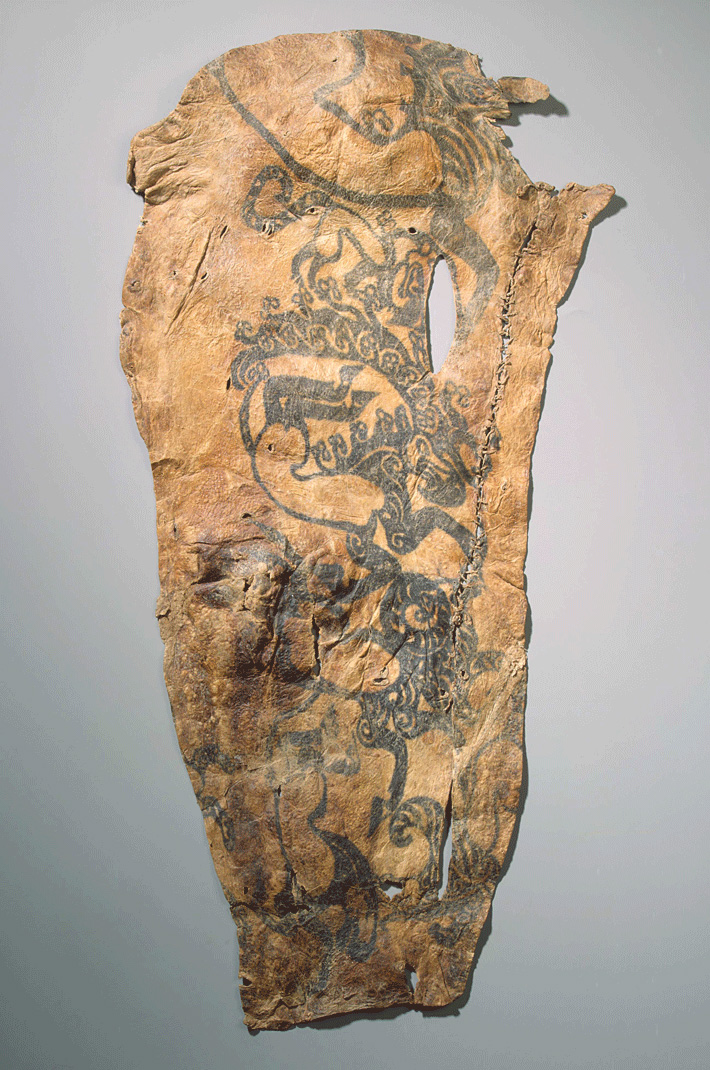
Some of the most spectacular tattoos in the ancient world have been found adorning Iron Age mummies unearthed in the Altay Mountains of Siberia. There, a series of tombs dug into permafrost preserved the remains of nobles from a nomadic people today known as the Pazyryk Culture. On the skins of these mummies were intricate tattoos, depicting both mythical and real animals in action: running, stalking victims, or twisting in an S-shape, which scholars call “the pose of agony.”
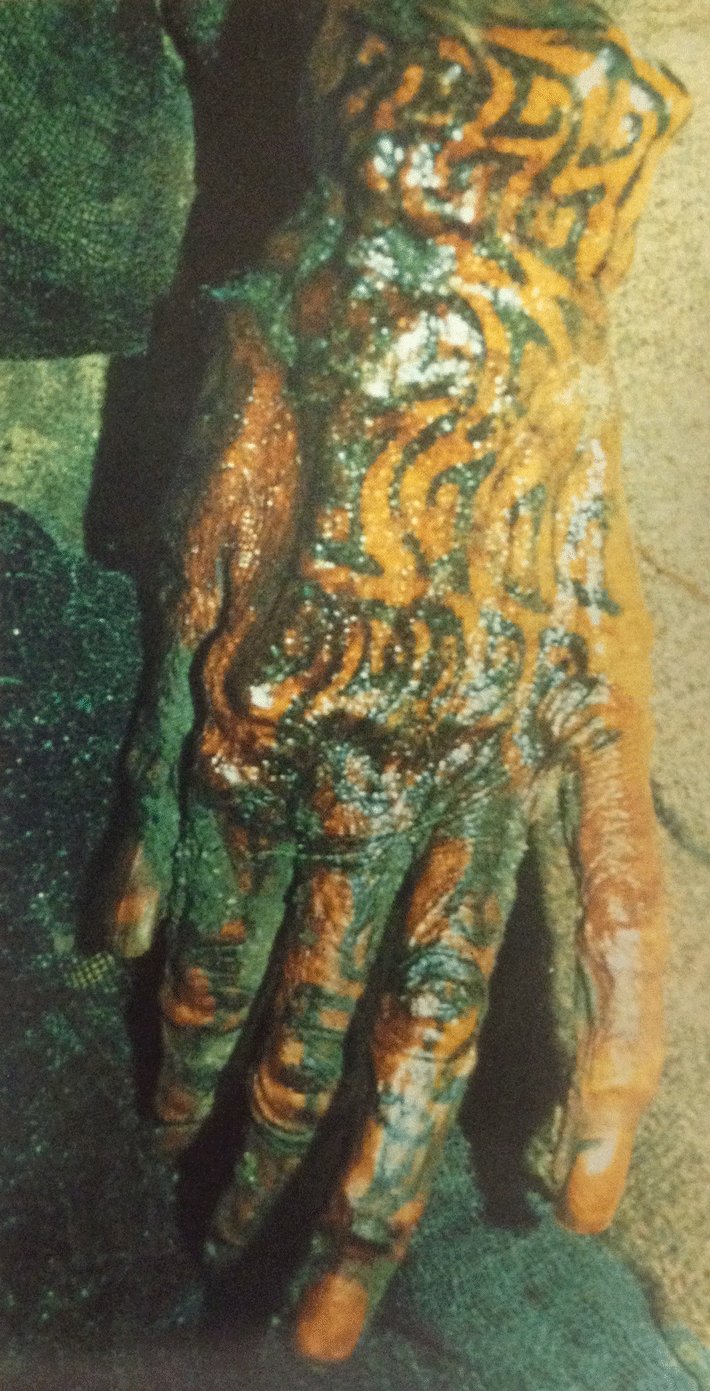
Archaeologist Sergey Yatsenko of the Russian State University for the Humanities says the animal most commonly found was a monster that took the form of a wild goat with an eagle’s beak and a panther’s tail. This creature appeared on the upper part of the right shoulder of most of the mummies. On the left shoulder, the Pazyryk people sported the depiction of a tiger or a wild ram. A rooster poised for battle was frequently tattooed on noblemen’s forefingers, and a group of goats or rams often marched along their lower legs.
Yatsenko points out that Greek accounts of the period stress that “barbarians” in Eurasia never went nude or even semi-nude in public, so most of these tattoos would probably have never been seen by others. Why endure the long and painful process of getting such dramatic tattoos if they were always covered? “I think they were for magical protection,” says Yatsenko, whose favorite Pazyryk tattoos are abstract designs found on the hands of a man who was probably a shaman. “Those tattoos were probably his spiritual weapons.”