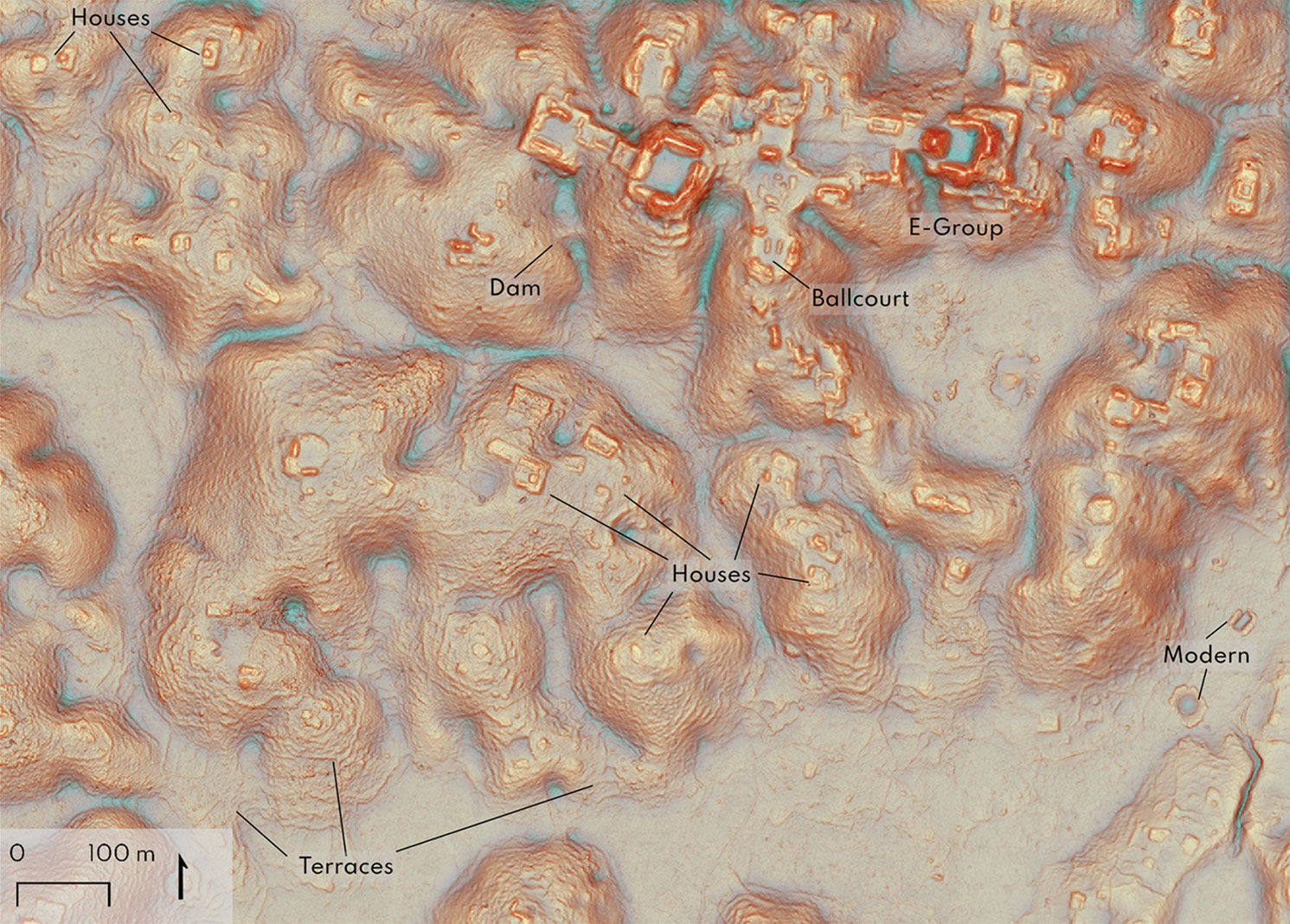
INDONESIA
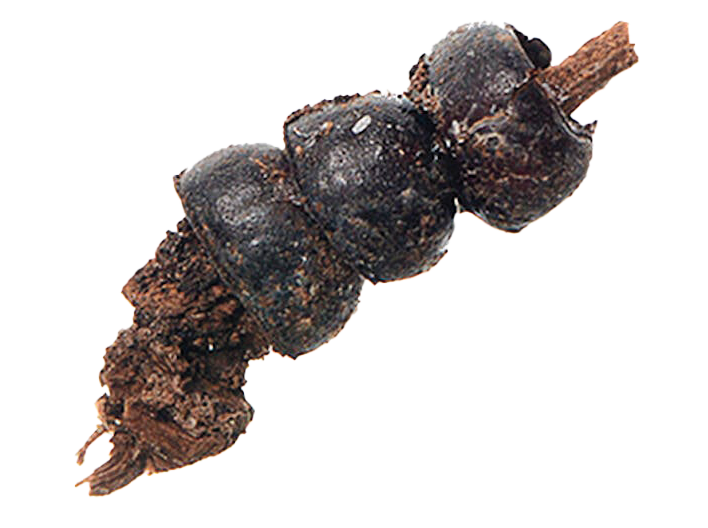
Experts have long debated when the first people traveled from Asia to Oceania. New evidence from Mololo Cave on Waigeo Island in the province of Southwest Papua indicates that early seafarers navigated to the island at least 55,000 years ago. Archaeologists unearthed stone artifacts and animal bones attesting to human occupation in the cave at that early date. They also found a small object made from tree resin—likely used as a fuel source—which is the oldest plant-based artifact found outside Africa.
Related Content

JAPAN
Crib sheets can come in handy, something people knew at least as long as 1,300 years ago. Recent infrared scans of a nondescript wooden object discovered more than 20 years ago at the former Japanese capital of Fujiwara-kyo revealed faint mathematical equations, such as 9 x 9 = 81. Researchers believe the 6.4-inch-long, half-inch-wide strip is a fragment of a larger multiplication table, the oldest ever found in Japan. It was likely used by government officials to estimate taxes, perform administrative duties, and even calculate the dimensions of burial mounds.
Related Content

AZERBAIJAN
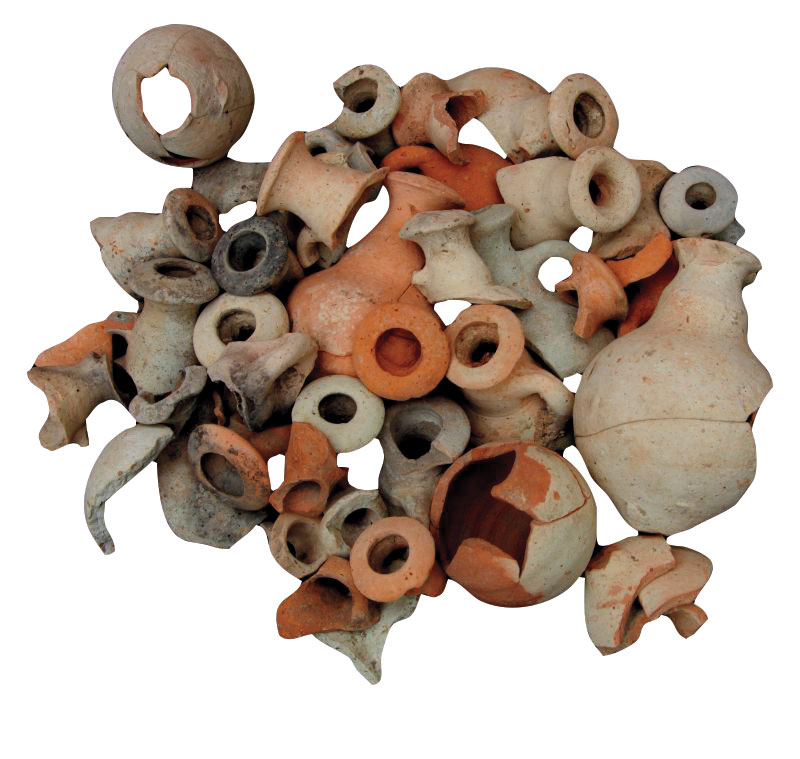
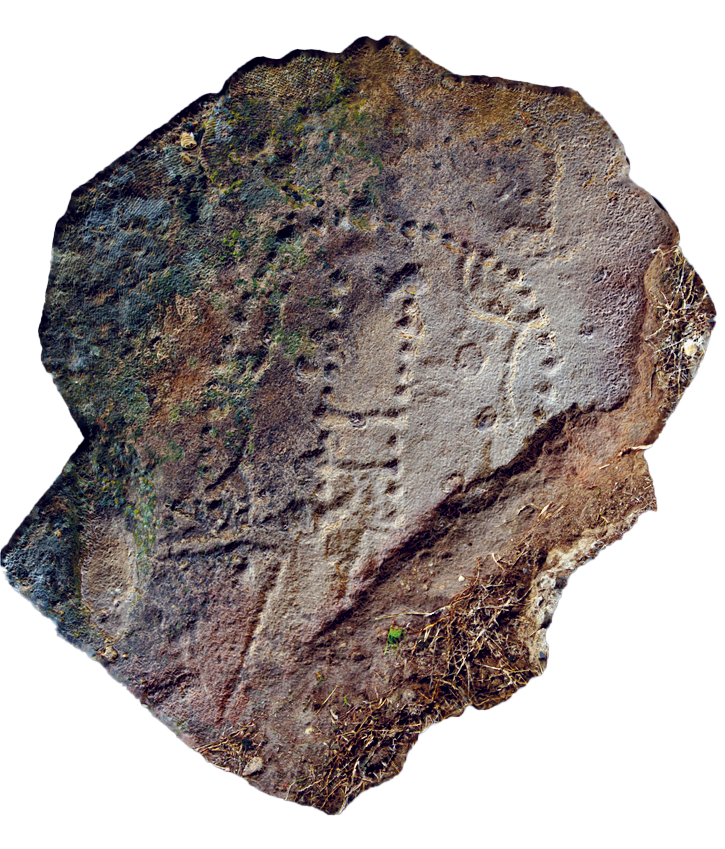
The game known as 58 holes, sometimes called hounds and jackals, was popular across cultures from northern Africa to western Asia. The game was thought to have originated in Egypt, where the earliest known boards date to the 2nd millennium b.c. However, new research has identified at least 6 stone game boards from the Absheron Peninsula on the Caspian Sea that are centuries older than those found in Egypt, suggesting the game may have first been played in the region.
Related Content
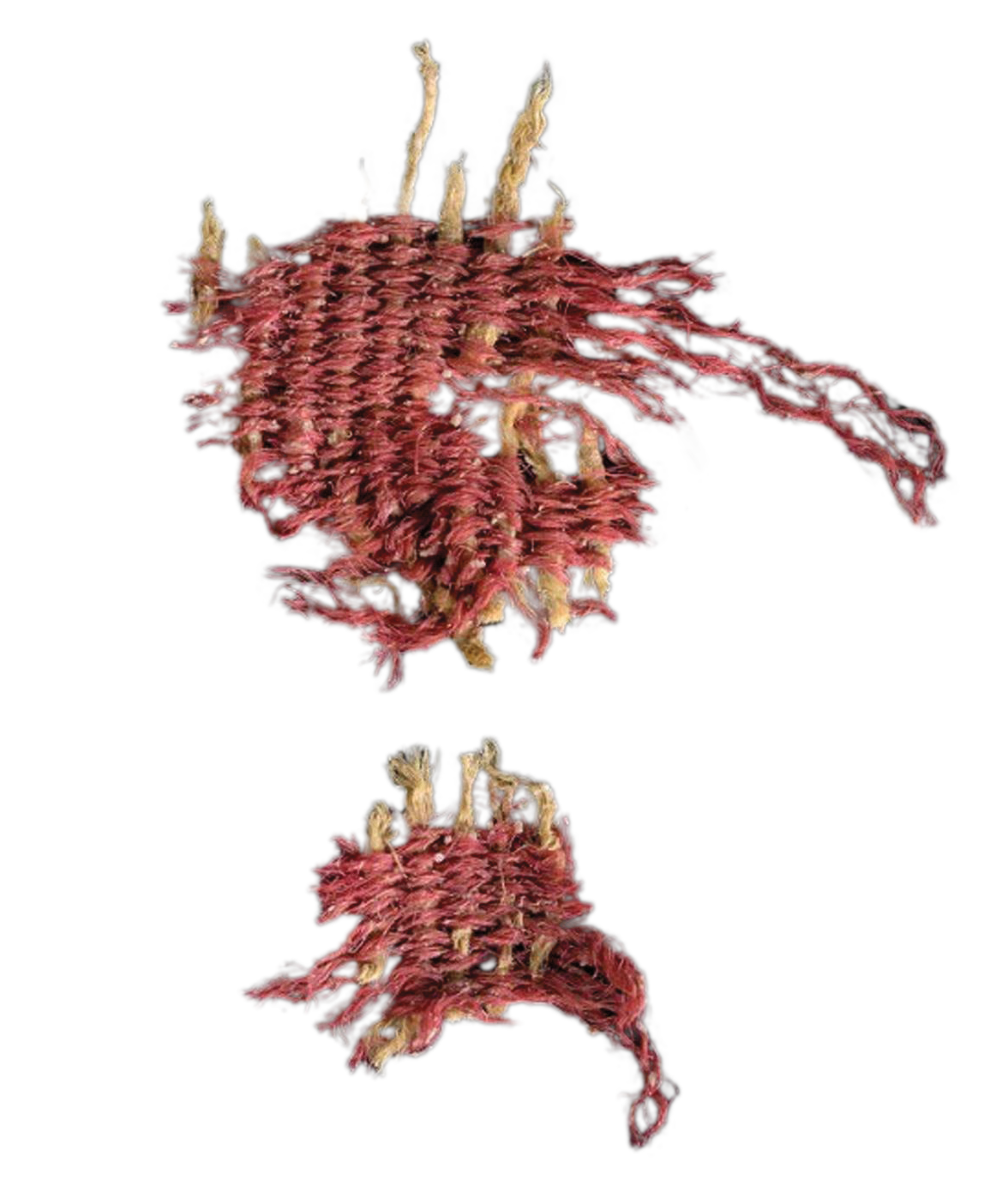
ISRAEL
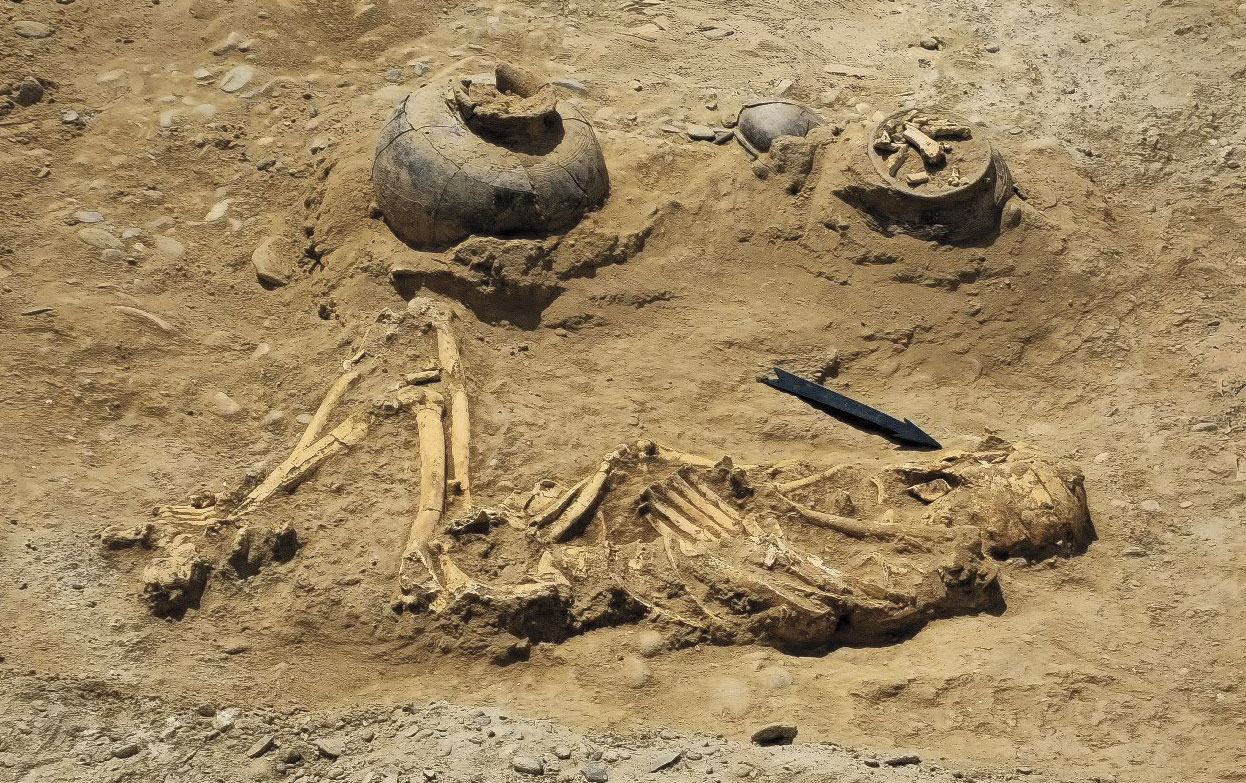
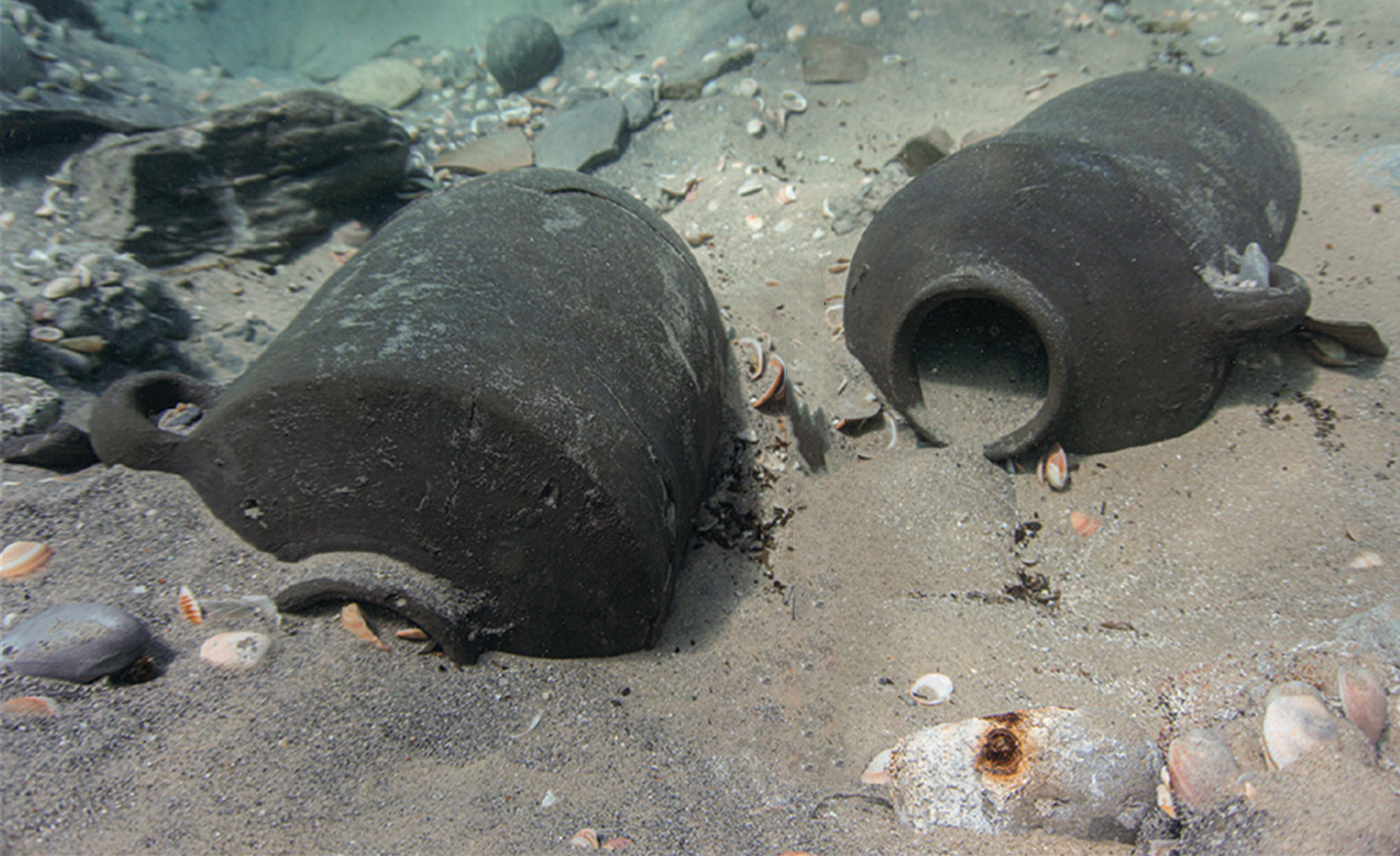
Some bugs truly have us seeing red, especially Kermes vermilio, a species of insect that was used to dye fabric scarlet. The earliest evidence of this practice comes from a tiny scrap of 3,800-year-old textile discovered in the Cave of Skulls in the Judean Desert. The coveted dye could only be produced during a single month of the year, after kermes females laid their eggs and before they hatched. The word “crimson” is derived from “kermes.”
Related Content
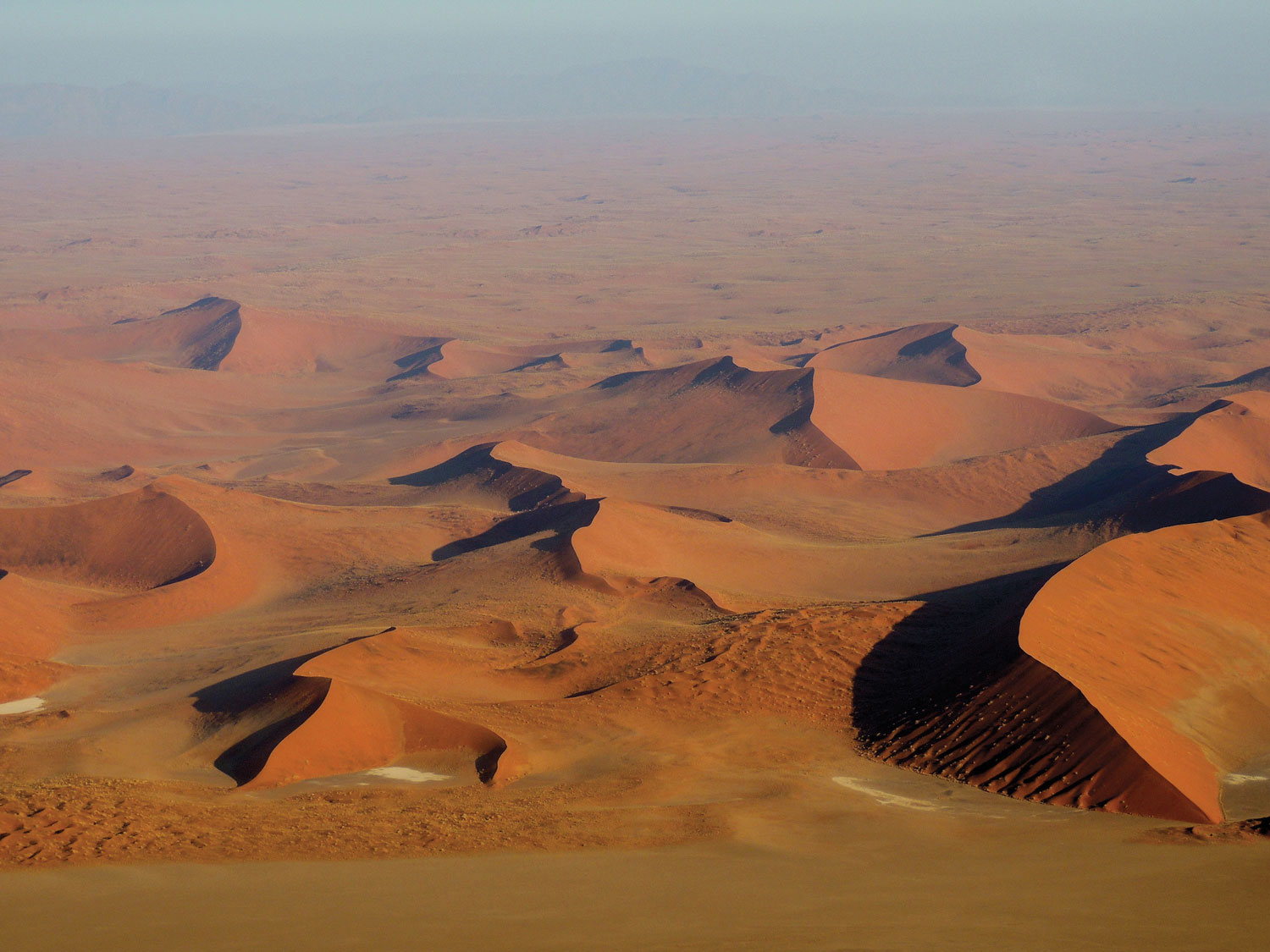

NAMIBIA
The Namib Sand Sea, home to 350-foot-tall sand dunes, receives so little rainfall that it is almost uninhabitable. Scholars believed it had been this way for millions of years—but this turns out not to be the case. New research at a site called Narabeb identified layers of mud beneath the sand that were deposited by an ancient freshwater lake. Fragments of stone tools found nearby suggest that early humans visited Narabeb occasionally between 200,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Related Content
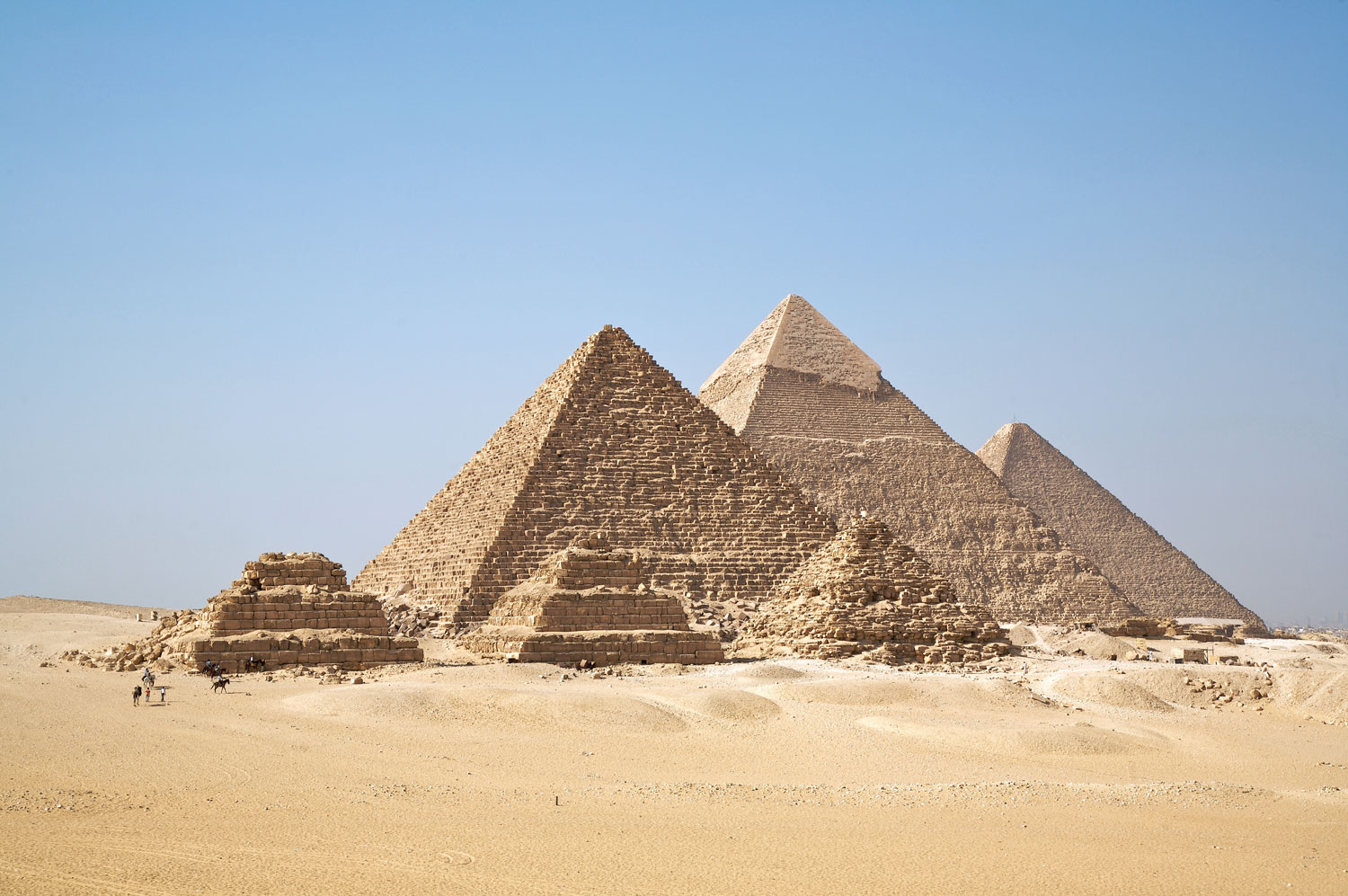

EGYPT
Construction of the Giza pyramids required a massive quantity of metal tools. Evidence shows that these tools were manufactured using a process with harmful consequences for the local environment and people. Chisels and other implements were created from copper that was often alloyed with arsenic, resulting in the release of toxins. Analysis of sediment sampled near Giza indicates that, at the height of pyramid construction around 2500 b.c., heavy metal contamination was 5 to 6 times normal, exposing laborers to deadly health risks.
Related Content
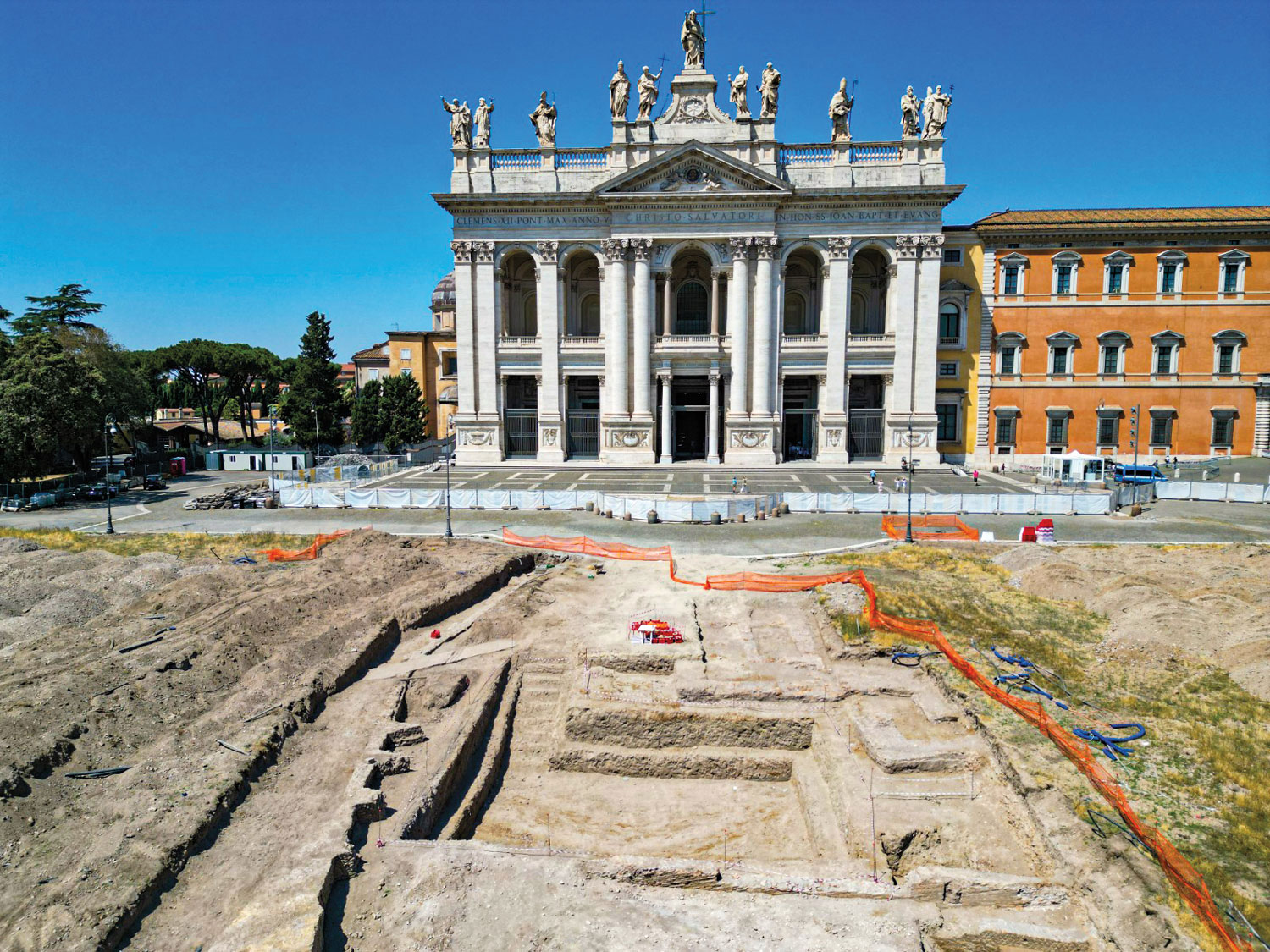

ITALY
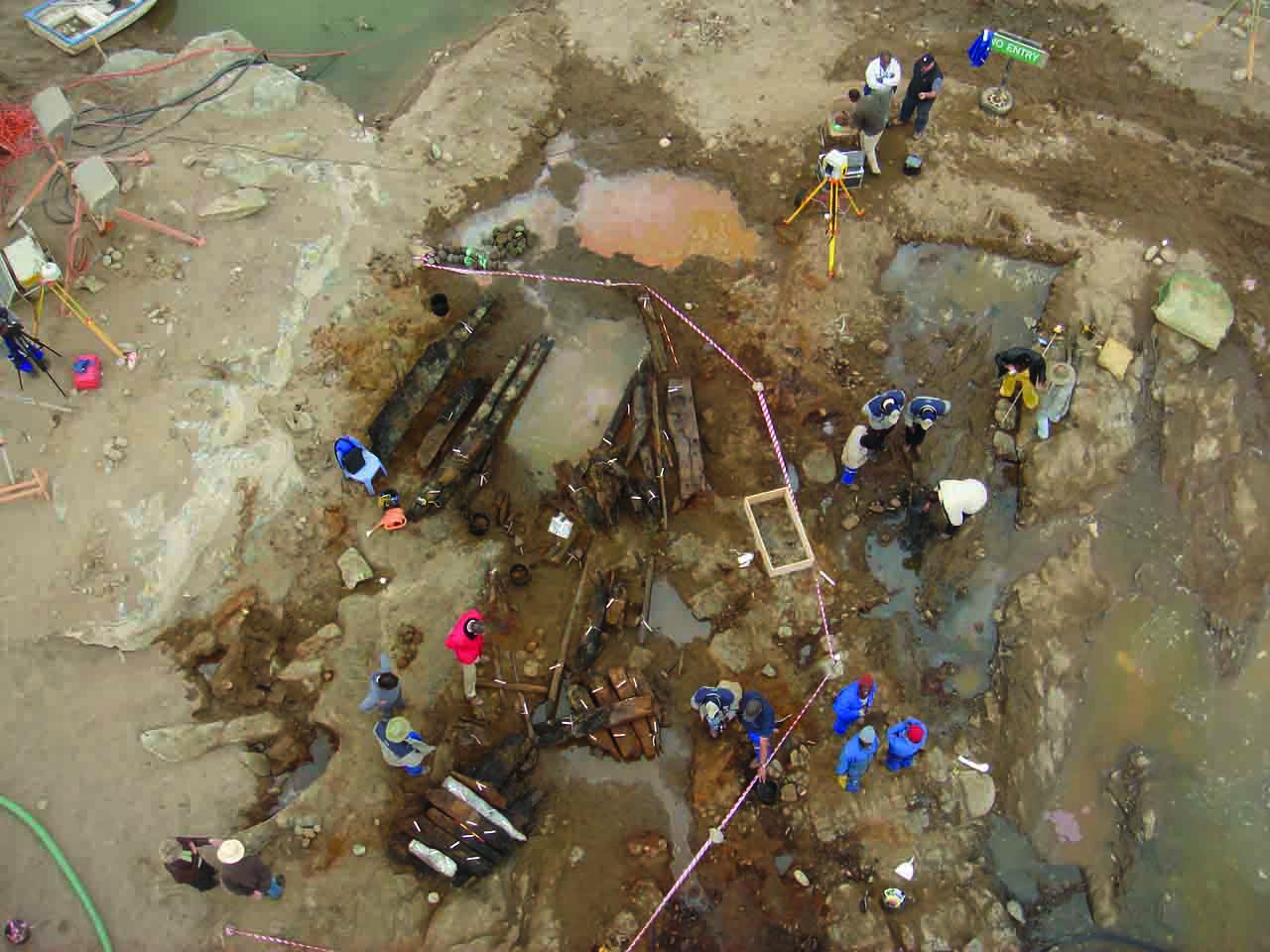
Excavations outside the Archbasilica of St. John Lateran in Rome revealed walls of a papal palace dating to the 9th century a.d. The sprawling complex was founded in the 4th century a.d. after the Roman emperor Constantine converted to Christianity. It was expanded and remodeled over the following centuries. The Lateran palace was the home of the papacy until the 14th century, when it briefly moved to Avignon, France, before relocating to the Vatican, where it remains today.
Related Content
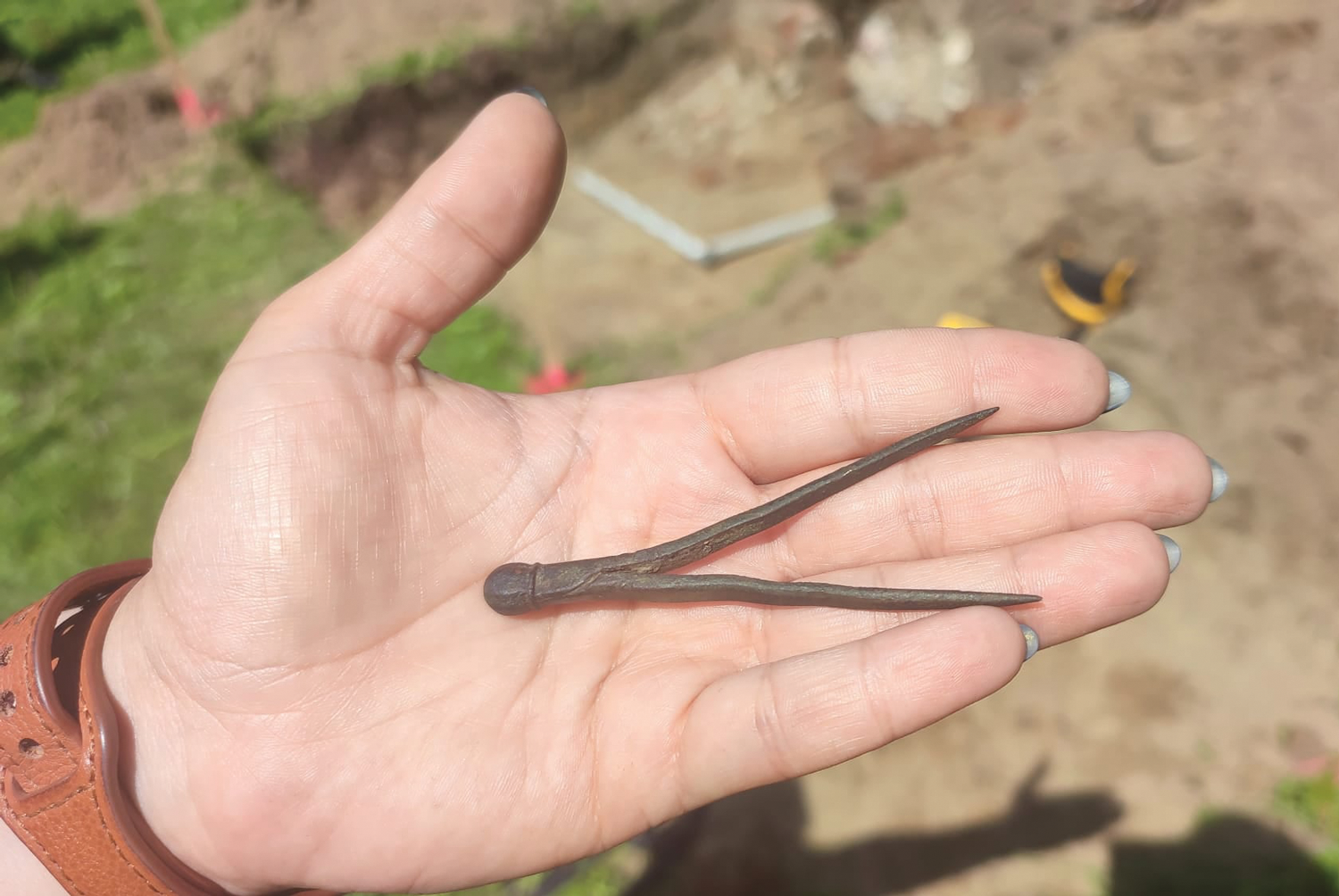

POLAND
A small instrument used to take precise measurements may have once belonged to a giant in the field of astronomy. While investigating tunnels beneath gardens in the city of Frombork in the region of Warmia, archaeologists discovered a 16th-century bronze compass. Nicolaus Copernicus was canon of Warmia and often made astronomical observations on the property, making it likely he used the device in his scientific endeavors. Copernicus, who died in Frombork in 1543, developed the heliocentric model of the solar system.
Related Content
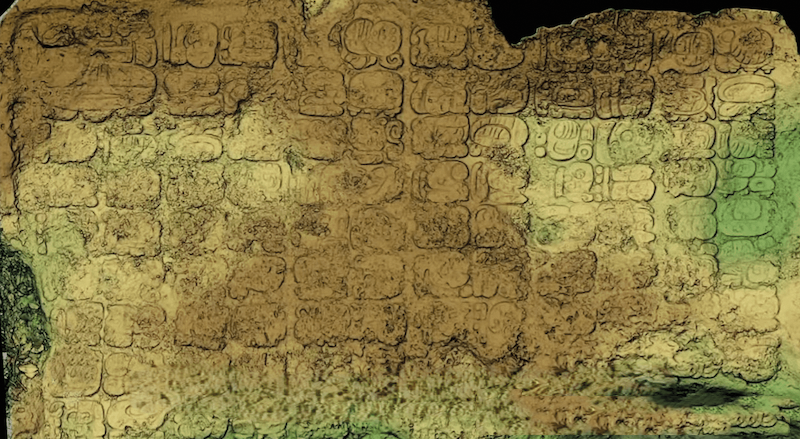
MEXICO
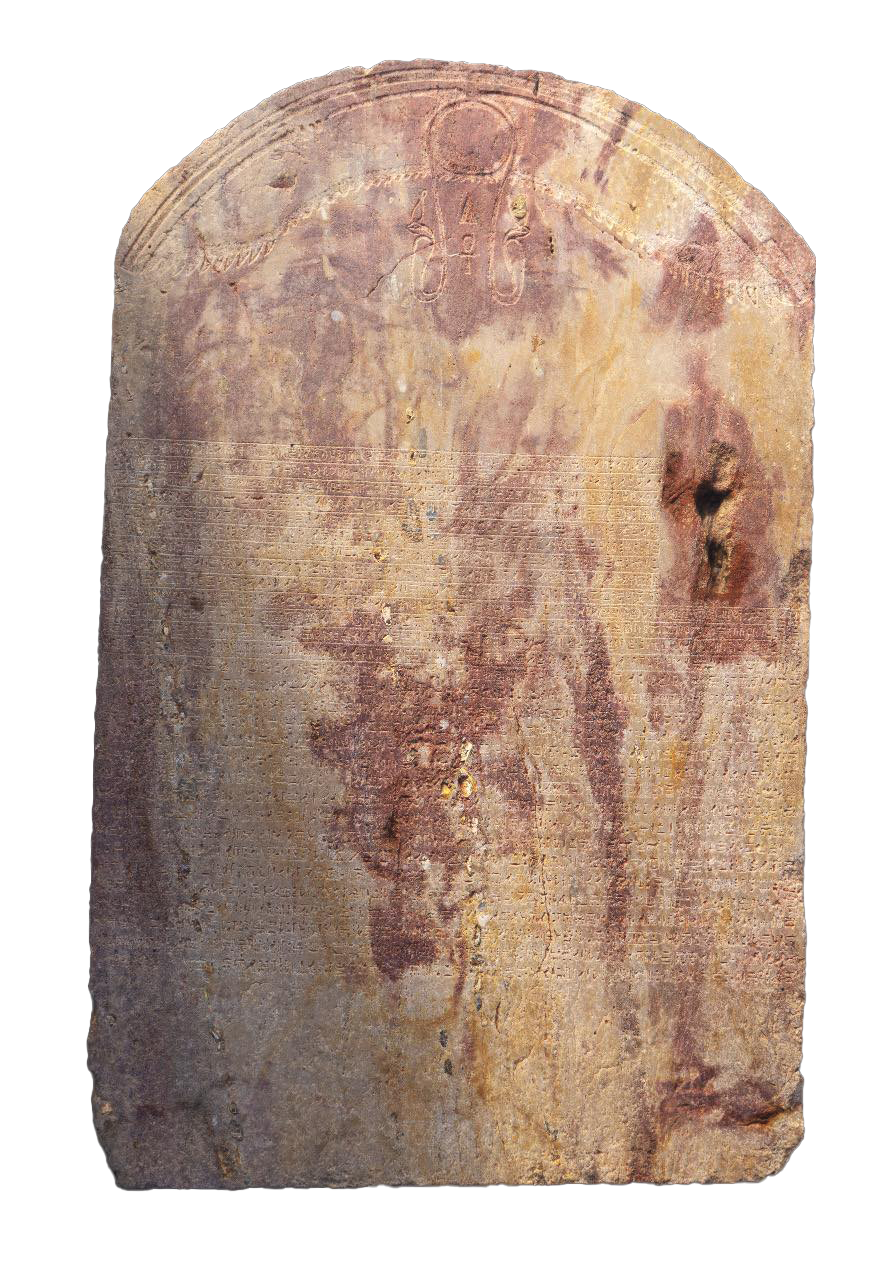
Between a.d. 600 and 1000, the Maya city of Cobá was inhabited by 50,000 people and was home to Nohoch Mul, the second tallest pyramid on the Yucatán Peninsula. Off a causeway connected to the temple, archaeologists recently discovered a panel including 123 Mayan glyphs carved into the rock floor of a sacred pool. These glyphs describe the founding of a town called Keh Witz Nal on May 12, a.d. 569. They also reference a previously unknown Maya ruler named K’awill Ch’ak Chéen.
Related Content

MASSACHUSETTS
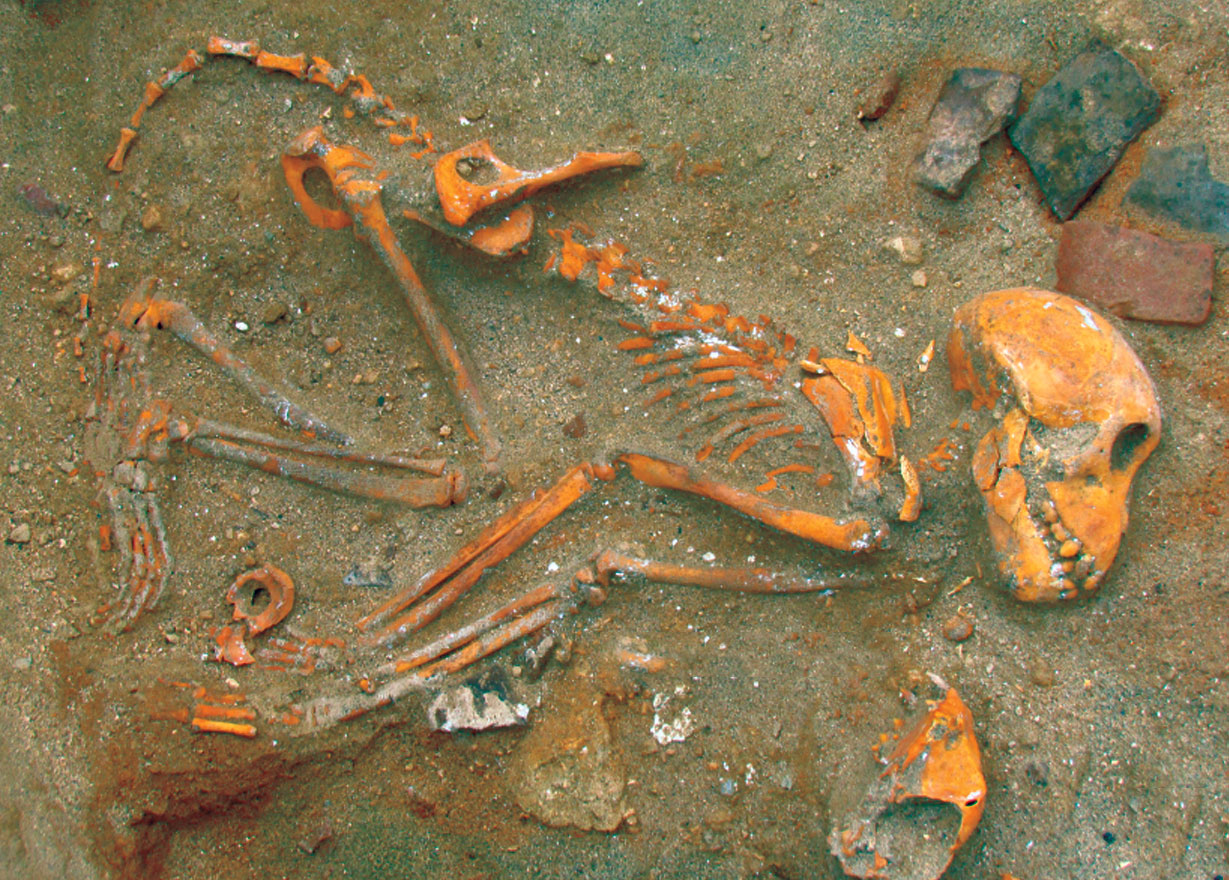
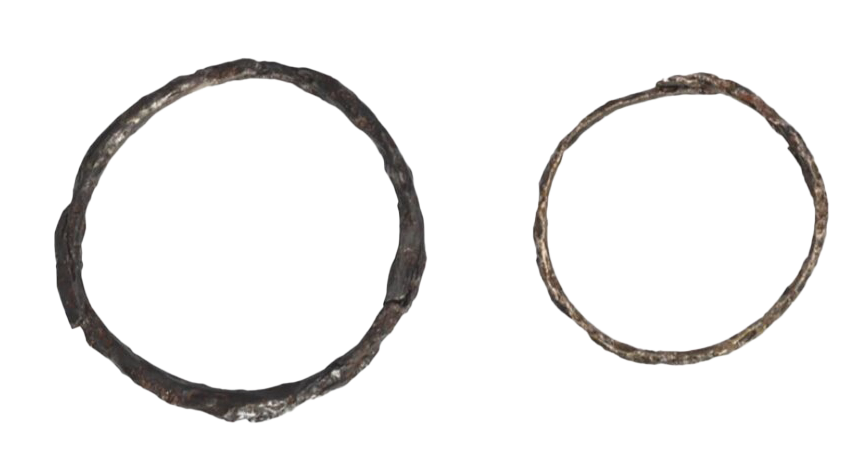
Five musket balls fired the day of the historic “shot heard round the world” were recovered from a battlefield in Minute Man National Historical Park. On April 19, 1775, British Regulars marched from Boston to Concord to seize colonial military contraband and encountered resistance from local militia members. The musket balls were likely fired by the patriots at British soldiers amassed near Concord’s North Bridge, although they apparently missed their mark. The day’s events led to the outbreak of the American Revolution.