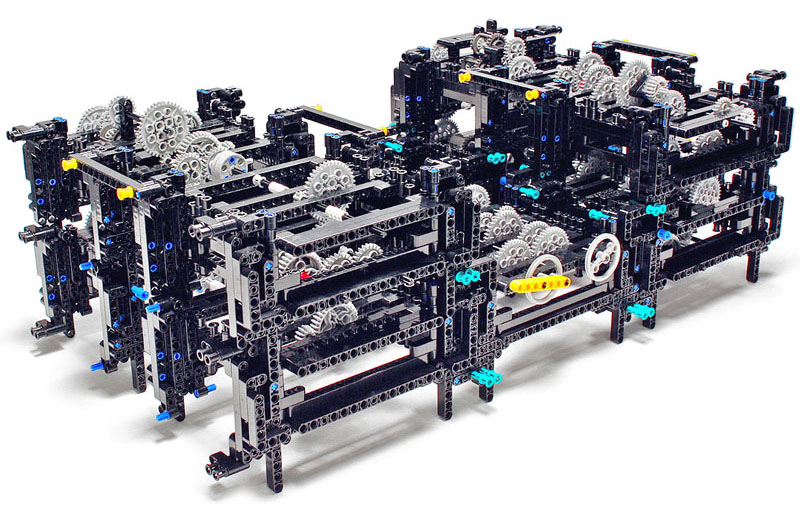
What is it?
A working Lego model of the Antikythera Mechanism
Date
Finished in May 2010
Material
Lego Technic
Number of Legos
More than 1,500
Originally Discovered
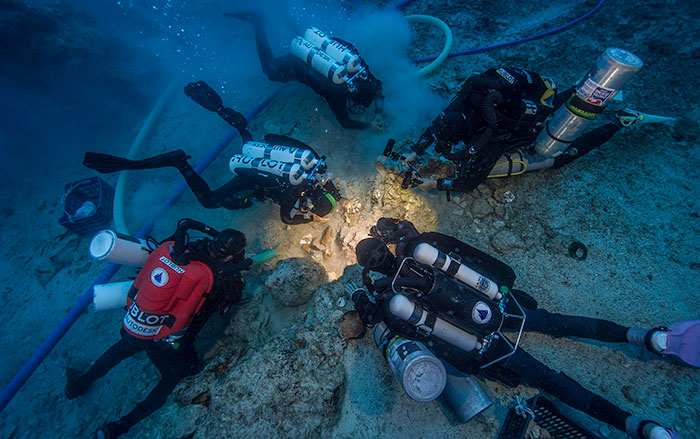
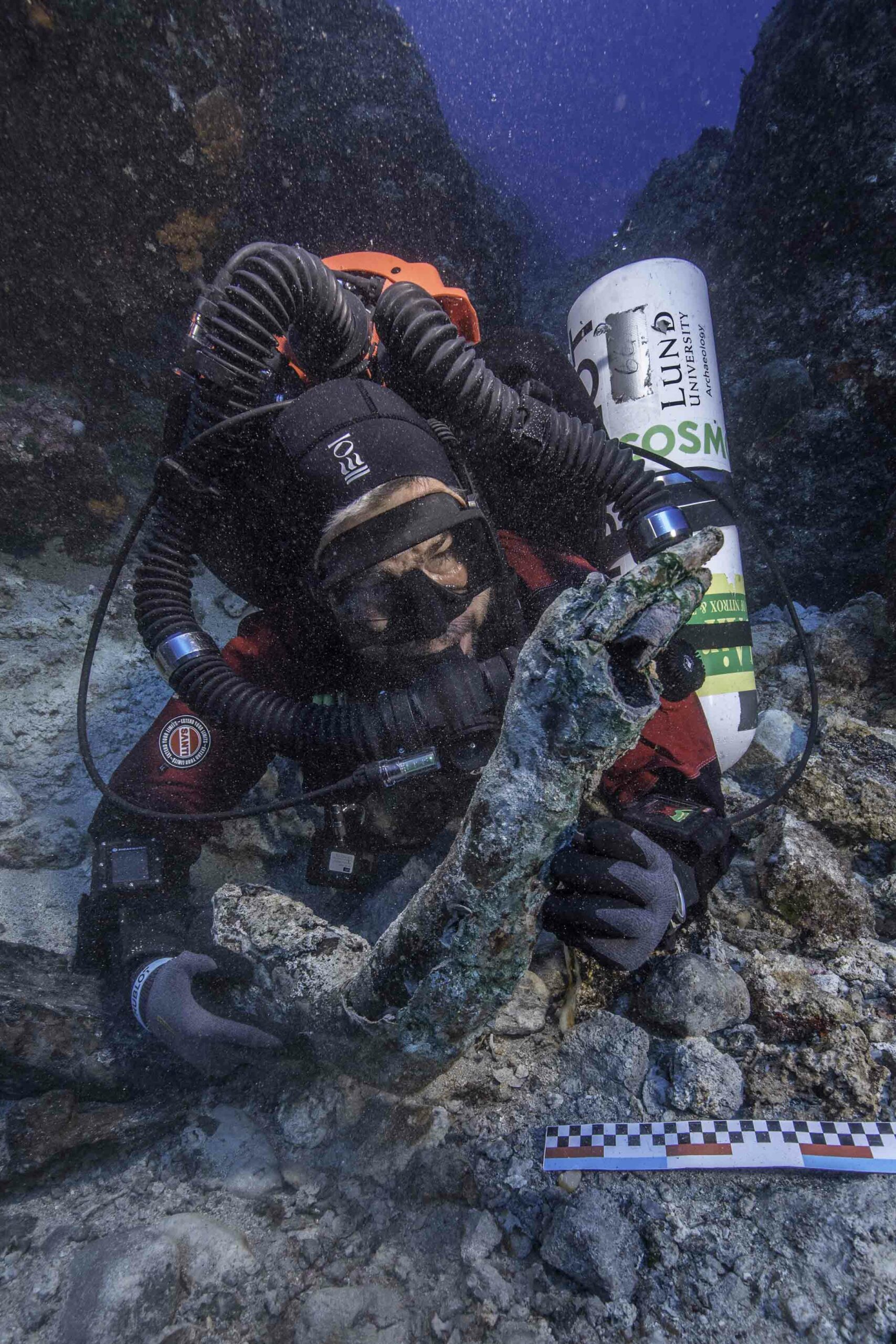
1901, in a shipwreck near the Greek island of Antikythera
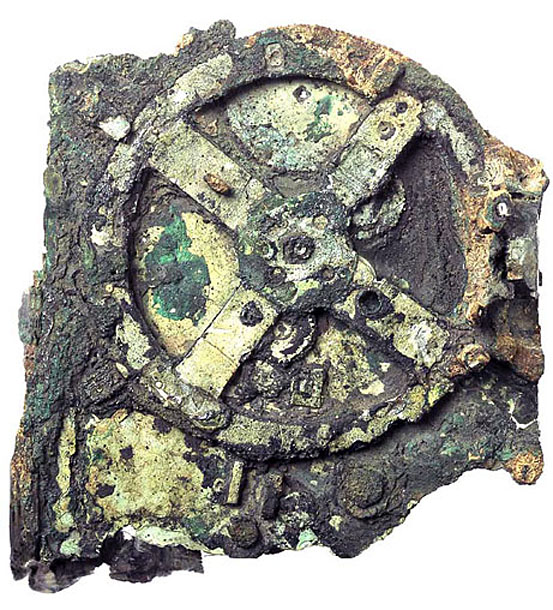

(© Antikythera Mechanism Research Project)
It took Andrew Carol 30 days to build a working model of the Antikythera Mechanism—the ancient Greek world's most sophisticated astrological instrument. The original device, dating to the second century B.C., consists of bronze gears. Carol used Legos.
The choice of medium limited Carol, but it illustrated the elegant simplicity of its inspiration. The Greeks could economically perform the math needed to calculate upcoming solar and lunar eclipses using 30 hand-cut gears with between five and 223 teeth—223 is the number of lunar months between eclipses. The Lego Antikythera does its calculations in a less direct manner, requiring more than 100 prefab gears assembled into several modules, each performing separate bits of math. Then seven differentials—additional gears—reconcile the computations from different modules.
The original Antikythera Mechanism is not only simpler than its Lego counterpart, it's more accurate. Carol's device can predict an eclipse to within 24 hours. The original is precise to within 12, thanks to a clever assembly that causes one of its gears to spin faster at some points in its rotation and slower at others, approximating the elliptical orbit of the moon. "Nothing on this planet was as mechanically complicated as the Antikythera Mechanism until the 1300s," says Carol. "It's a testament to the Greeks' genius."











