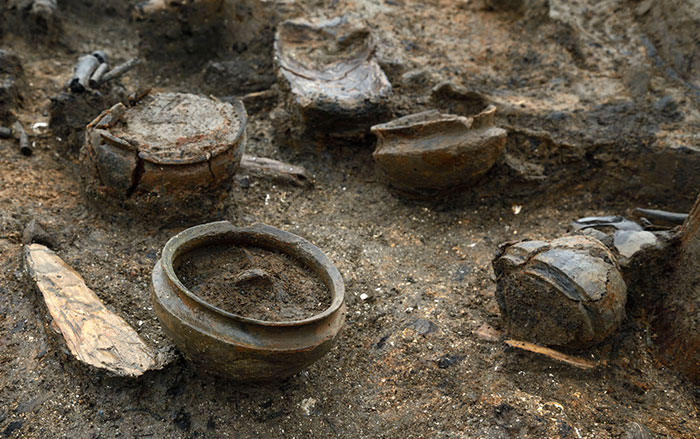
Scientists are still exploring the mysteries of one of the deadliest pandemics the world has ever known: the Black Death, the medieval disease outbreak that killed millions in Europe between 1347 and 1351. At the time, it was attributed to bad air—some kind of generalized pestilential miasma. Today, blame is believed to reside with Yersinia pestis, the bacteria that causes plague, though the historical pandemic was clearly more virulent— and faster-spreading—than any modern version of the disease.
Several recent DNA studies have confirmed the presence of Y. pestis in medieval graves across Europe. The most recent work in the field is examining its genome to sort out what exactly made the older version of the plague different. The study, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, examined the remains of 100 plague victims buried near London. It reveals that the Black Death was caused by a previously unknown variant of Y. pestis that no longer exists. But the multinational team has not yet found the specific genetic reason for the difference in plague virulence between then and now. "The search goes on," says study coauthor Jim Wood of Pennsylvania State University.










