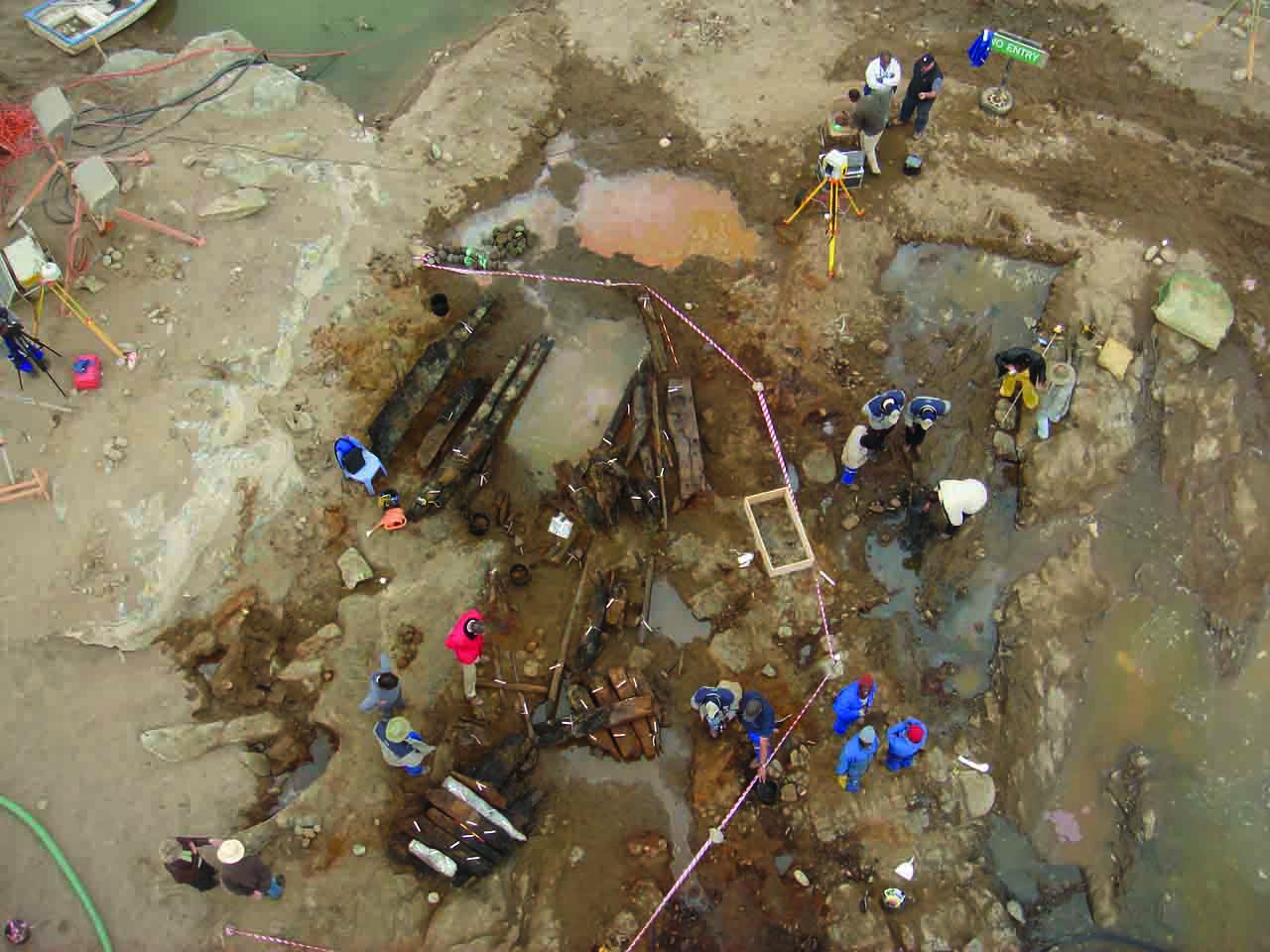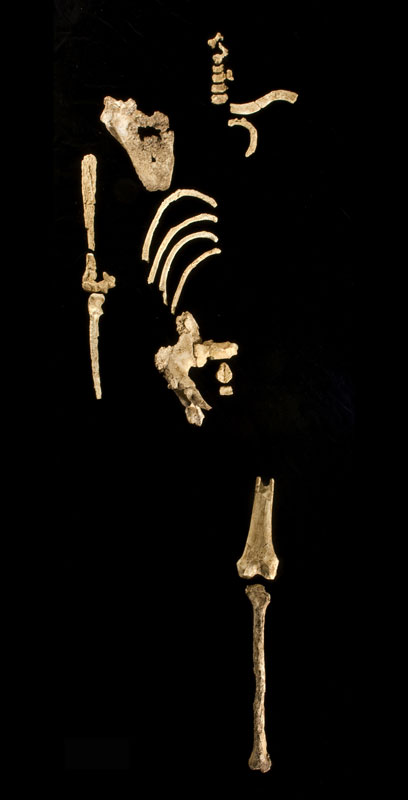
For the last 35 years, the short-legged “Lucy” skeleton has led some scientists to argue that Australopithecus afarensis didn’t stand fully upright or walk like modern humans, and instead got around by “knuckle-walking” like apes. Now, the discovery of a 3.6-million-year-old beanpole on the Ethiopian plains—christened “Kadanuumuu,” or “Big Man” in the Afar language—puts that tired debate to rest. The new fossil demonstrates these early human ancestors were fully bipedal.
Many dozens of A. afarensis fossils have been uncovered since Lucy was discovered in 1974, but none as complete as this one. Kadanuumuu’s forearm was first extracted from a hunk of mudstone in February 2005, and subsequent expeditions uncovered an entire knee, part of a pelvis, and well preserved sections of the thorax.
“We have the clavicle, a first rib, a scapula, and the humerus,” says physical anthropologist Bruce Latimer of Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio, one of the co-leaders on the dig. “That enables us to say something about how [Kadanuumuu] was using its arm, and it was clearly not using it the way an ape uses it. It finally takes knuckle-walking off the table.” At five and a half feet tall, Kadanuumuu would also have towered two feet over Lucy, lending support to the view that there was a high degree of sexual dimorphism in the species.