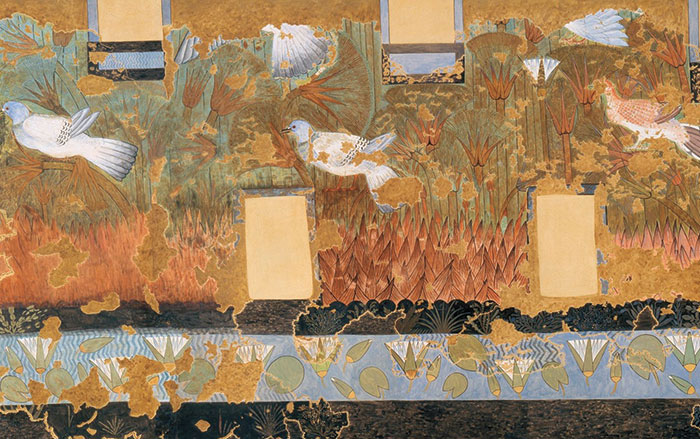
As early as the Predynastic period, beginning in the mid-fifth millennium B.C., the Egyptians placed wine jars in tombs as offerings to the dead. References to wine dating to the 1st and 2nd Dynasties have been identified on ceramic jar seals found in the burial grounds at Abydos and Saqqara, and the word for wine, “irp,” appears on 2nd Dynasty stelas. By the 4th Dynasty, in the mid-third millennium B.C., tomb designers had begun to illustrate viticulture and winemaking on tomb walls. For archaeologist Sofia Fonseca of the Autonomous University of Barcelona, such imagery offers valuable insights into the vintner’s entire process. “We have this idea that viticulture and winemaking originated in the ancient Near East, and that European wine culture is a legacy from Greece and Rome,” she says. “But the truth is that, starting more than 4,500 years ago, and for the next two millennia of Egyptian history, we have images that show a traditional process similar to those winemakers in Mediterranean regions are still using. By studying these images, we can have a real change in the paradigm of wine history and bring awareness to the influence that Egyptian wine culture had on Mediterranean wine culture.”
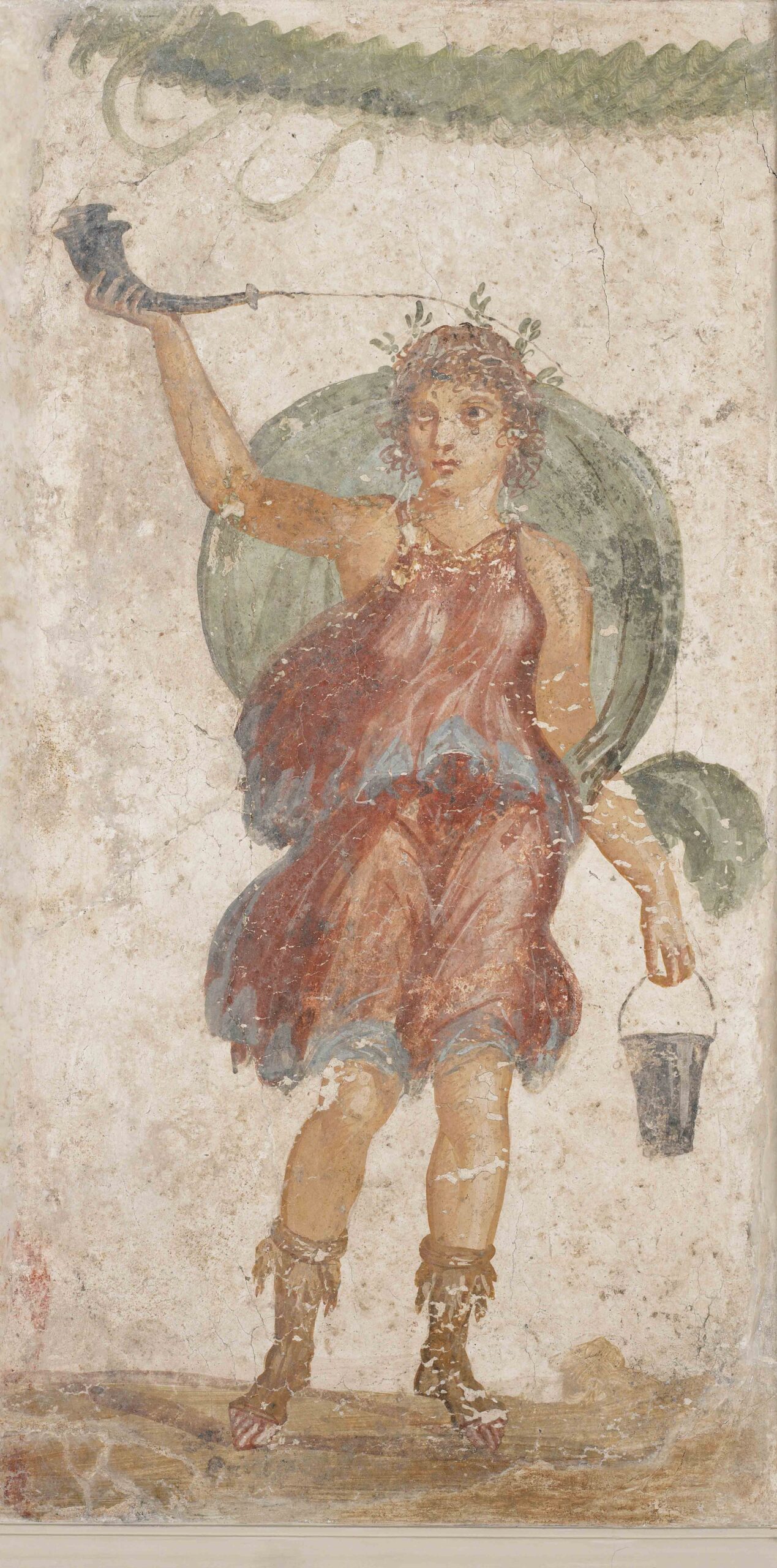
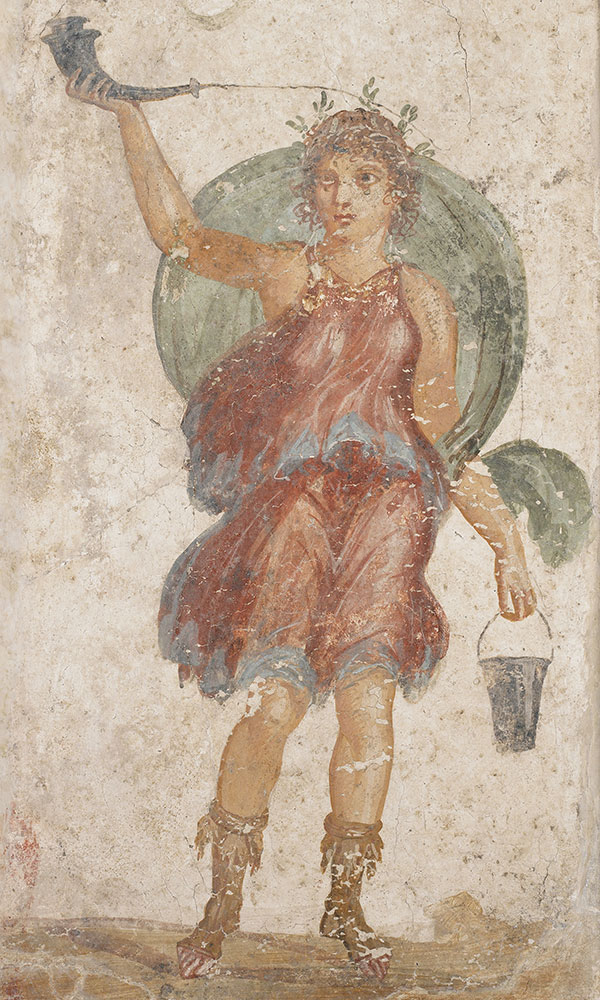
While the Egyptians drank both red and white wine, only red wine is depicted in the tombs. “It’s interesting to see how the symbolism of wine is deeply related to the color red,” says Fonseca. “This recalls the relationship between wine and the blood of Osiris, the god of death and resurrection, who is called the Lord of Wine in the late Old Kingdom Pyramid Texts. It also recalls the relationship between wine and the reddish color of the Nile during the annual flood, when iron-rich sediment flows into the river from the mountains of Ethiopia at just the time when the grape harvest begins.”