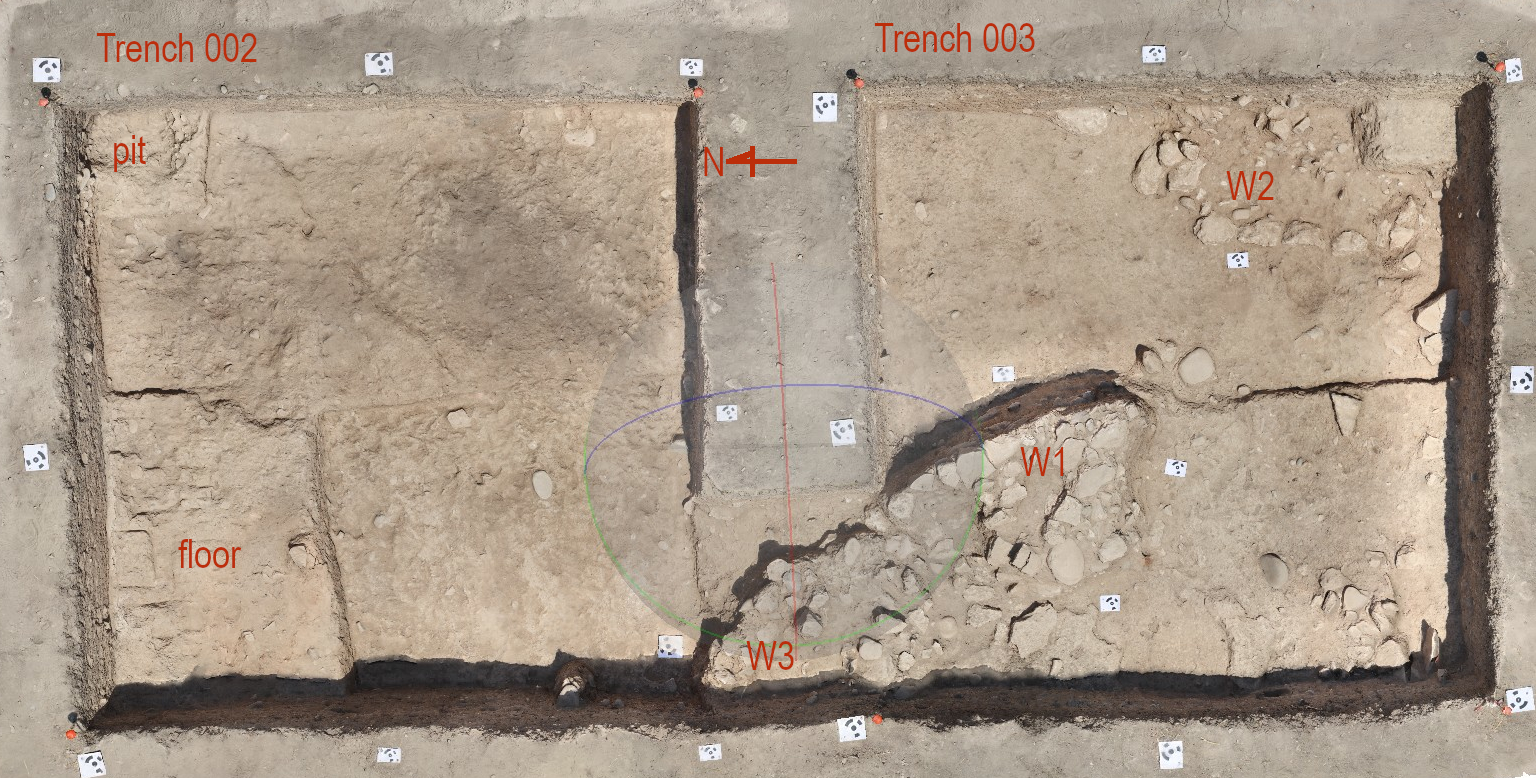
ERIMI, CYPRUS—KNews reports that a team of researchers led by Giorgos Vavouranakis of the University of Athens has completed an excavation at Erimi Pamboula, an archaeological site in southern Cyprus occupied between 3500 and 2900 B.C. The recent investigation uncovered the floor of a house with a pit and a platform, the wall of a circular structure, and a pit containing burned deer bones and antler fragments. Stone tools, unfinished jewelry pieces and a figurine made of the green or grey stone picrolite, and decorated pottery dated to the early third millennium B.C. were also recovered. To read about prosperous Bronze Age merchants on Cyprus, go to "In the Time of the Copper Kings."
Excavation Concludes at Prehistoric Settlement on Cyprus
News October 9, 2025
Recommended Articles
Digs & Discoveries January/February 2022
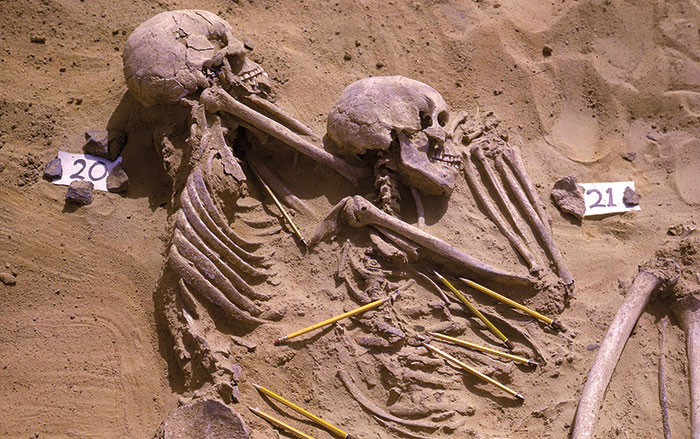
The Roots of Violence

Digs & Discoveries September/October 2020
Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow
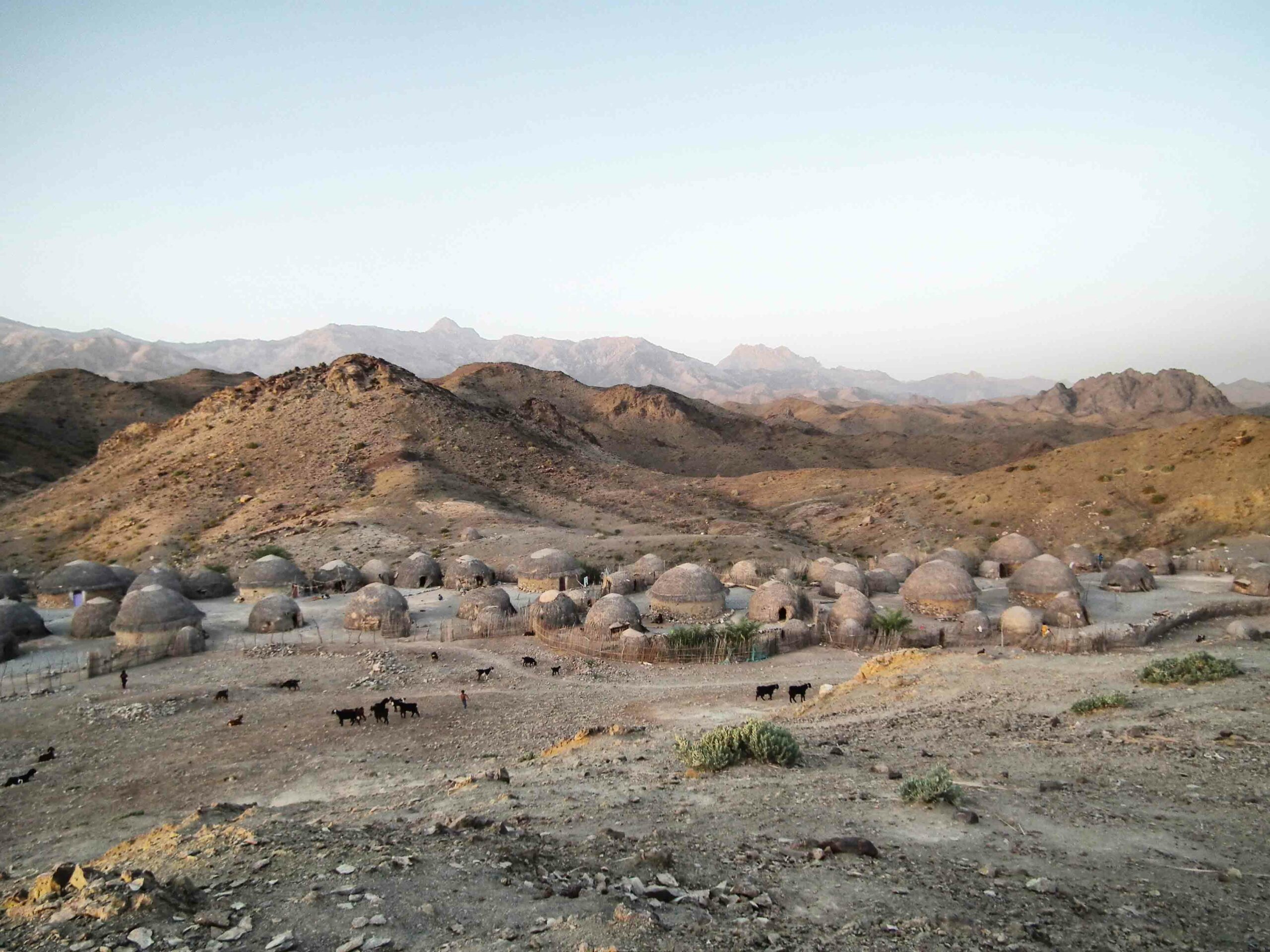

Digs & Discoveries May/June 2016
The First Casus Belli
Model Homes March/April 2026
Doorways for the Dead
LOCATION: Thebes, Egypt
DATES: Ca. 1981–1975 b.c.

-
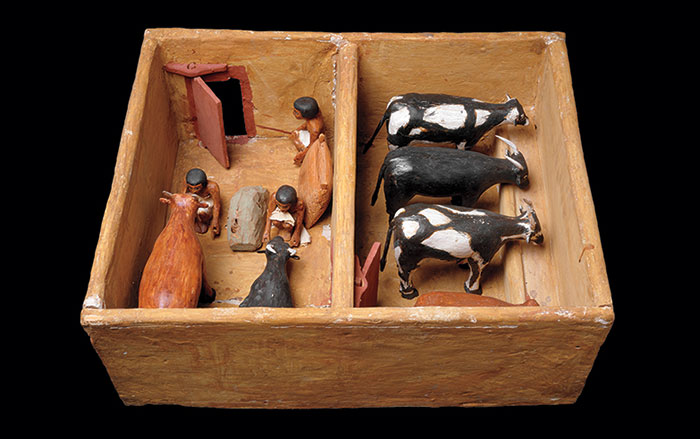
Features September/October 2025
Spirit Cave Connection
The world’s oldest mummified person is the ancestor of Nevada’s Northern Paiute people
 Howard Goldbaum/allaroundnevada.com
Howard Goldbaum/allaroundnevada.com -
Features September/October 2025
Here Comes the Sun
On a small Danish island 5,000 years ago, farmers crafted tokens to bring the sun out of the shadows
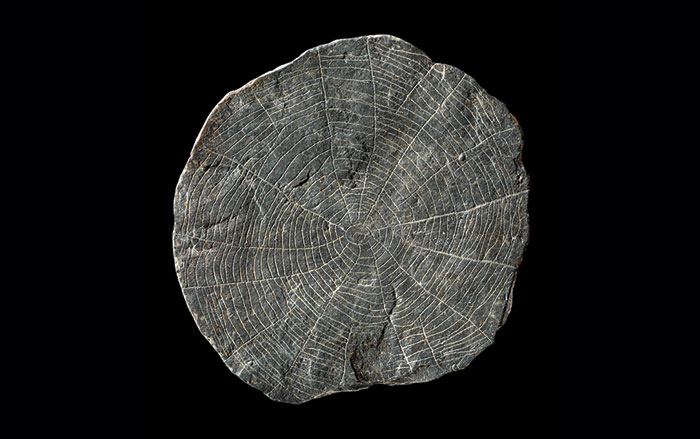 Courtesy the National Museum of Denmark
Courtesy the National Museum of Denmark -
Features September/October 2025
Myth of the Golden Dragon
Eclectic artifacts from tombs in northeastern China tell the story of a little-known dynasty
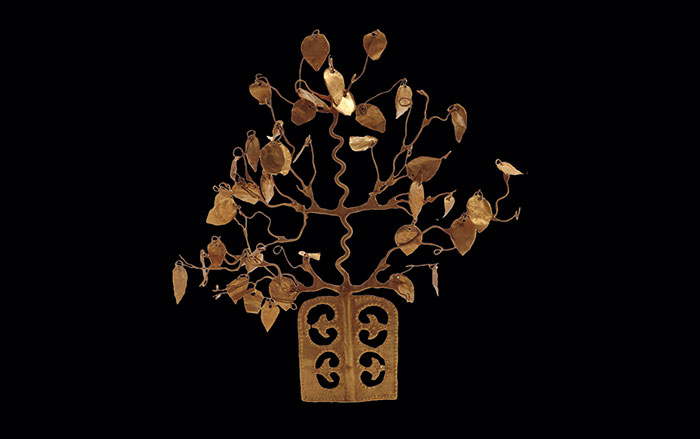 Photograph courtesy Liaoning Provincial Museum, Liaoning Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology, and Chaoyang County Museum
Photograph courtesy Liaoning Provincial Museum, Liaoning Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology, and Chaoyang County Museum -
Features September/October 2025
Remote Sanctuary at the Crossroads of Empire
Ancient Bactrians invented distinct ways to worship their gods 2,300 years ago in Tajikistan
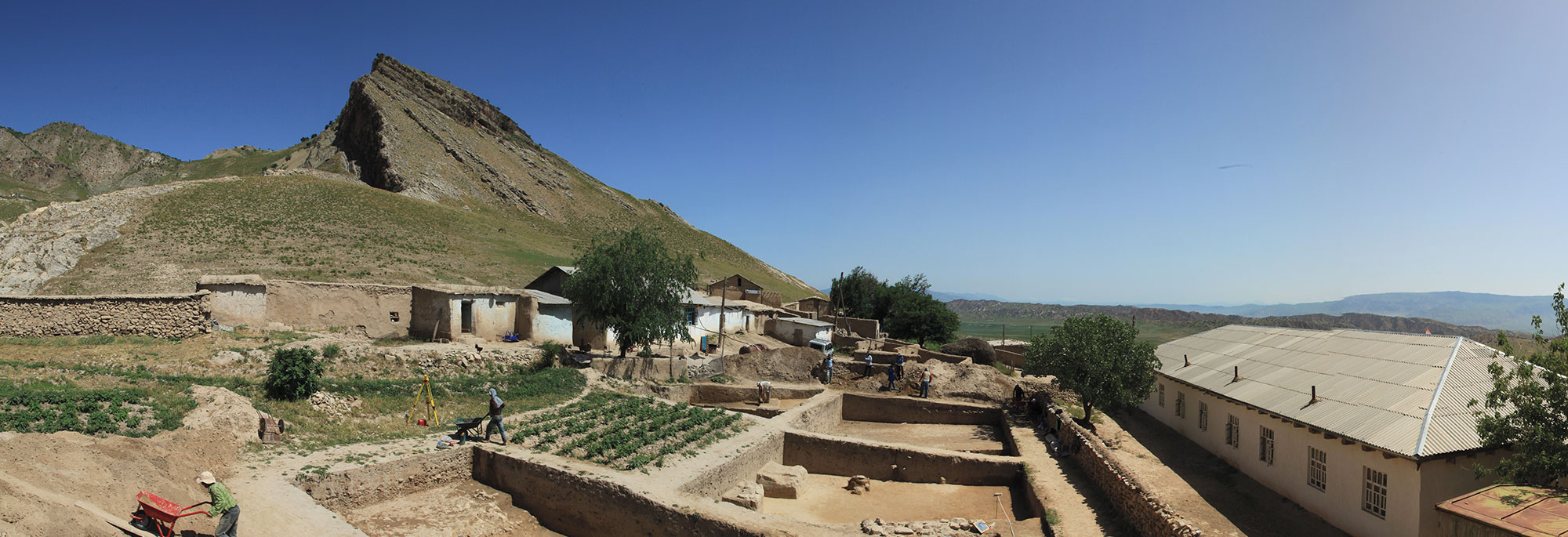 Gunvor Lindström/Excavations supported by the German Research Foundation
Gunvor Lindström/Excavations supported by the German Research Foundation



